Almost all modern computers and laptops come with SSDs instead of hard drives. SSDs make our systems snappier and help with faster file movements. With a slower SSD, a “storage bottleneck” will be created, resulting in a bad overall performance. This doesn’t only happen with hard drives but also with slow SSDs. But, there are signs that you can easily detect indicating the need for an SSD upgrade.
Secondary storage, i.e., HDDs or SSDs, has a key role in providing the necessary data for the CPU to work on any task. This data is first loaded into the RAM so that the CPU gets faster access to it. This is because RAM is way faster than the fastest SSD out there. So, faster secondary storage always means that the CPU doesn’t have to wait for the data to arrive. However, a slow SSD or a hard drive will make the CPU wait longer for the required data. This will make your computer sluggish. Now, the signs of a slow storage drive are clear, and they clearly indicate that you need a storage upgrade, especially to a faster SSD than what you are currently using. So, let’s talk about all those signs.
1. Slow Booting and shutdowns
In order to boot up the system, the BIOS/UEFI looks for the bootloader in the boot drive (typically in MBD or GPT). The bootloader is a program with different names in different OS, like Windows Boot Manager or GRUB in Linux. It is responsible for loading the operating system with all the files. A slow HDD or SSD will delay the process of reading the bootloader, adding extra seconds before the operating system even starts to prepare. The core part of the OS, called the Kernel, is also loaded by the bootloader, which prepares important files like drivers and system files.
Basically, the OS relies on the storage drive (SSD or HDD) to load the system files, and a slow drive can heavily impact the booting process. After this, the OS has to load the user data, software data, startup programs, etc, and for everything, data is required, and when the storage medium is slow, everything will be slow.
The same goes for the shutdown process. When we close our system, the operating system has to save the important files, close the running processes, and terminate the background processes. All this requires a huge amount of data to be safely saved on the primary storage because RAM can’t store the data permanently. However, a slow booting process will never be alone andwill come together with slow shutdowns as well.
Now, booting and shutdown times also depend on the total size of data on your computer, installed applications, and overall use. But some numbers can be considered.
What is considered a “slow” booting time?
| Boot Time | High-End Computer (SSD) | Normal Computer (HDD/SSD) |
|---|---|---|
| Excellent | 5-15 seconds (NVMe SSD) | 10-20 seconds (SSD) |
| Good | 15-30 seconds (SATA SSD) | 20-40 seconds (SSD/HDD mix) |
| Borderline | 30-45 seconds (HDD or unoptimized SSD) | 40-60 seconds (HDD) |
| Bad | 45+ seconds (HDD or OS issues) | 1-2 minutes (Slow HDD, many startup apps) |
| Terrible | 1+ minute (Failing HDD, OS corruption) | 2+ minutes (Aging HDD, serious OS issues) |
If your system falls in the terrible category, your system is crying for an SSD upgrade and you should do it ASAP. Here is a guide on how to choose the right SSD for your computer.
2. Slow Program and Games Loading

If your web browser, games, photo editing software, video editing software, etc, take too long to load up, this can be another signal you need an SSD upgrade. Again, the data required to open and run those programs is stored in your primary storage drive, i.e., hard drive or solid-state drive. So, if the drive is slow, these programs and also the games will take a long time to load.
Whenever you try to open a program or game, the operating system first locates the .exe (on Windows) or .app file (on macOS). Along with that, cache files, configuration files, libraries, fonts, images, and many other things are required even to prepare a program for loading. So, how fast a program loads will depend on how fast this information is provided to the operating system. A slower drive means a longer waiting time for the OS for those important files.
This is called High-seek time, which is much higher in hard drives compared to even the normal SATA SSDs.
How Long is Too Long for a Program to Load?
Here’s a realistic expectation of load times on different storage types for common applications:
| Application | HDD Load Time | SATA SSD Load Time | NVMe SSD Load Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Chrome | 5-10 sec | 1-2 sec | <1 sec |
| Photoshop | 20-40 sec | 5-10 sec | 2-4 sec |
| Microsoft Word | 8-15 sec | 2-4 sec | <2 sec |
| Call of Duty (Game) | 1-2 min | 20-30 sec | 10-15 sec |
Now, if you open a program frequently, it will boot up faster compared to the first boot. In modern computers, if a browser like Google Chrome is taking more than 10 seconds to load, you seriously need to upgrade your system with an SSD. The numbers given in the table may vary depending on other specifications, like the CPU and RAM. But, I believe you have got the point, which is that if the data required to open a program is taking too long to be found, the storage medium should be upgraded.
3. Freezing and Stuttering
Both stuttering and freezing are critical signs of performance issues in any computer. Stuttering is small lags or you can say frame drops, while using your computer, but the computer will keep running. However, freezing is when the system or the program you are using stops responding completely. In Windows, you get a (Not Responding) notification, and the program may get blurred out. Now, a faulty or slow storage drive isn’t always the reason behind the problem because a full RAM can also cause the same problem.
However, most of the time, this happens because of the delay in accessing the important files while an operation is running. Even if the RAM is filled up, the operating system can use your hard drive or SSD as a page file or virtual memory. But, when the RAM is full and the hard drive is slow, restarting is normally your last resort.
How to confirm if a slow or faulty drive is the culprit?
The first method is to check the drive usage in the Task Manager’s performance tab. If the disk usage is generally higher than 80% or higher, there is some issue with the drive.
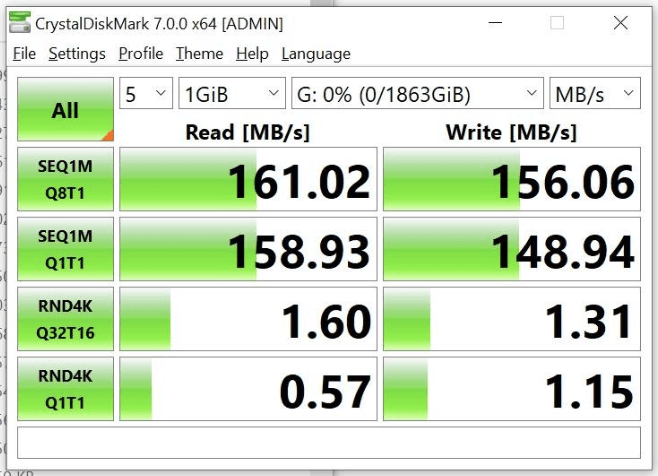
Another great way is to do a simple drive benchmark using benchmark software. Just do a simple CrystalDiskMark test and see how well your drive performs. If you think the drive is slower, especially the random performance, it means the stuttering and freezing are happening due to a slow drive and it needs an upgrade.
4. Slow File Reading and Writing
This one is obviously the clear sign that your drive needs a replacement. The speed can get comparatively slower than before, or your workload has changed. If moving files here and there is an important thing in your daily work, you surely need an SSD upgrade. I am talking about data reading and writing because this is related to the sequential performance of your drive. All the things that we discussed above were related to the random data, which is mainly utilized for loading operating systems and running games, etc. However, if the raw data read/write speed is slower, you should upgrade to a new drive with higher sequential performance, especially.
In any of these cases, it is a clear sign that you need an SSD upgrade. Check for the fastest SSD that can fit in your computer, and get one to improve SSD read/write performance.

I think you are aware but I would like to highlight that the total read or write speed from one drive to another depends on the read/write speed of both the drives. For example, a flash drive with a maximum write speed of 500MB/s will not go beyond that even if the source SSD is a 5000MB/s drive.
5. High CPU usage when accessing files
Just look at the Task Manager whenever you try to open a program or load a game. If the CPU shows 100% or near its full capacity, this means the slow SSD results in the CPU waiting for the required data. It is called a system bottleneck, which is caused by a slow drive. Again, this is just a step to diagnose the issue. The symptoms are everything that we discussed above. So, if you are seeing your computer using your CPU at full capacity without any need, it could be a sign that you need an SSD upgrade.
6. Some BSOD Errors
Not all but some BSOD (Blue Screen of Death) errors directly indicate problems with your storage drive. Below are some of them:
1. UNEXPECTED_STORE_EXCEPTION
This BSOD error is caused by corruption in storage-related processes, such as NTFS file system errors or SSD firmware issues. Some read/write failures and sudden system crashes are the common symptoms from this error.
2. CRITICAL_PROCESS_DIED (0x000000EF)
This one is one of the most common errors that we see in Windows 10 and 11. Essential Windows processes (like wininit.exe or csrss.exe) fail due to disk corruption or read/write errors. However, disk problem isn’t the only cause as this issue can be caused by driver problems and RAM corruption.
3. NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM (0x00000024)
This BSOD error indicates issues with the NTFS file system, often due to bad sectors, corrupted MFT (Master File Table), or failing drive controllers.
4. KERNEL_DATA_INPAGE_ERROR (0x0000007A)
This error indicates that Windows failed to read kernel data from the disk into RAM due to bad sectors, partition problems, drive failure, or even a slow drive.
5. STATUS_DISK_OPERATION_FAILED (0xC0000185)
7. KERNEL_STACK_INPAGE_ERROR (0x00000077)
This is another issue related to the Kernel when Windows cannot load the required kernel data into memory due to disk corruption or bad sectors.
8. INACCESSIBLE_BOOT_DEVICE (0x0000007B)
When this error appears, it simply means Windows is unable to access the boot partition due to drive failure, corruption, or wrong AHCI/SATA settings.
7. Bad Gaming Performance
Most people think that gaming is just about a graphics card sending frames to the monitor and the faster it does that, the better will be the gaming experience. They think a faster NVMe will just help with faster booting, saving, streaming, loading, and quitting the game. But, that isn’t the case.
When you load the game, the required game data (models, shaders, textures, etc) are accessed from the primary storage device. Before it goes to the VRAM, it is temporarily stored in the RAM which acts as a buffer. Now, the CPU will prepare the data and send it to the GPU. The CPU also has the job of processing the game logic like physics and animations. All that requires faster access to the data. Now, the GPU will copy the data from the RAM into its VRAM. Now, this data is directly accessible for rendering.
A slow SSD or hard drive will result in longer load times. But, it can also result in lower FPS in asset-heavy scenes. The games which loads the textures and models mid-game can be heavily impacted by a slower storage medium.
I agree that GPU has the primary goal here but, in case, you think you have everything sorted out ranging from graphics card, CPU, and RAM, but still you can’t get the most out of your system, you might also look at the storage.
8. Your system has a specification mismatch
When a fast CPU is combined with slow RAM, it results in a bottleneck, and the CPU can’t work at its full potential. The same happens with the storage drives, i.e., Hard Drives and SSDs, as we discussed earlier. Example: You have a Core i7/i9 or Ryzen 7/9 with 16 GB+ RAM, but the system lags when loading files, apps, or games, it clearly means there is a mismatch in the storage specifications. You are probably using a slow SSD or worst, a hard drive.
Tools like PCPartPicker will help you decide on the right type of SSD based on the existing specifications. You just enter the existing parts like Motherboard, CPU, RAM, etc, and then look at what it suggests for the storage drive.
I hope this helps!