Affiliate Disclosure: This post may include affiliate links. If you click and make a purchase, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Yes, the Random Access Memory tends to degrade over time. The lifespan of the RAM varies widely depending on usage conditions, but a typical consumer DRAM is designed to last for several years, even under heavy operations. Generally, consumer RAM is expected to function reliably for 5 to 10 years under normal operating conditions.
Our computers and laptops use DRAM as the primary memory, and this DRAM is based on capacitors. Now, because capacitors can’t store charge permanently and require constant refreshing, the operation of DRAM becomes complex. RAM chips operate at very high frequencies, which also induces a lot of heat. So, the DRAM has all the elements that contribute to faster degradation and lower lifespan. However, the design of DRAM is so simple that memory chips can operate reliably for years under heavy load without any errors. A single memory cell in the DRAM comprises a transistor and a capacitor.
The memory read-and-write operations aren’t very destructive for both transistors and capacitors. However, certain factors may still contribute to faster degradation, including high temperatures and overuse. I want to discuss all of them and then show you how to eliminate them, making your RAM last longer.
Reasons for RAM degradation
RAMs are designed to operate in tandem with the CPU at a high speed for extended periods. Unlike long-term storage devices like SSDs and HDDs, RAM chips have little time to rest. The intensity of usage will decide your RAM’s degradation period. High-frequency and intensive usage, like gaming and heavy computational tasks, increases the number of reads and writes to the RAM. Over time, this can lead to the wear and tear of capacitors, transistors, and other components within your RAM.
Continuous high temperatures can also lead to the faster degradation of your RAM. This is because electronic components wear out more quickly when exposed to excessive heat for prolonged periods. This typically occurs due to inadequate cooling and high ambient temperatures. Over long periods, the RAM will degrade due to the normal aging of its components.
The electrical noises from the nearby components can also result in RAM degradation. Additionally, physical damage, manufacturing defects, electrical stress, power fluctuations, and software bugs can cause RAM damage, potentially leading to premature failures.
How to detect RAM degradation?
Run Memory Diagnostics in Windows
If your system is running on the Windows operating system, Windows has an excellent built-in tool to check the condition of your memory. You can easily identify your memory degradation if this tool highlights some errors or problems with your RAM. Let’s see how you can use it.
- Press Win + R to open the Run dialog. Type mdsched.exe and press Enter.
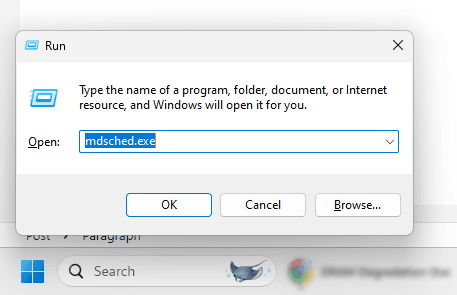
- Select “Restart now and check for problems” to perform an immediate test, or “Check for problems the next time I start my computer” for a scheduled test.
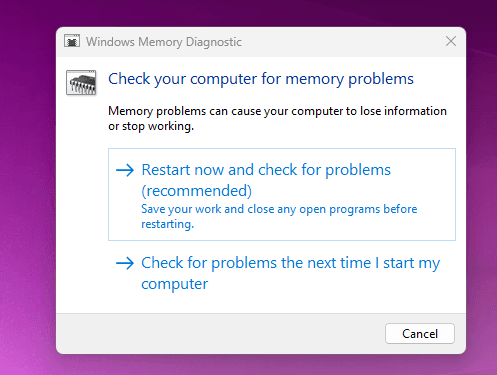
- Your computer will restart and run the test. It will take some time to complete.
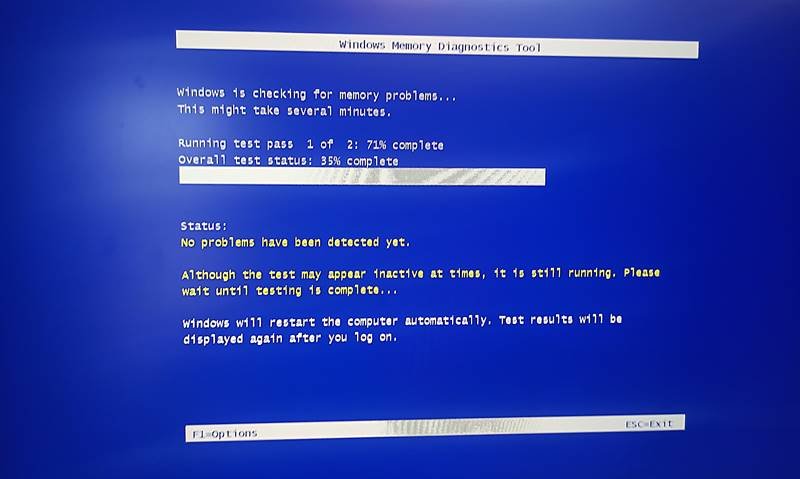
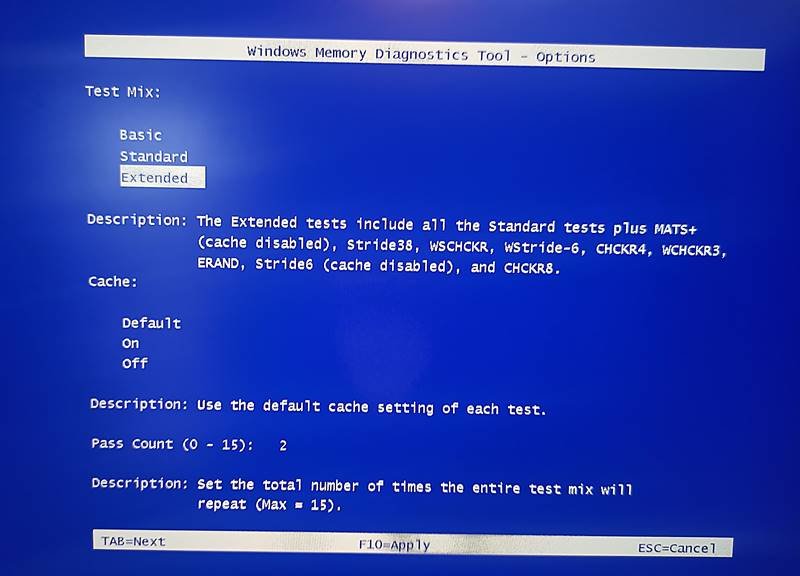
- Once the test page is there, you can also change the intensity of the test from basic or standard to advanced. You can open this menu by clicking F1.
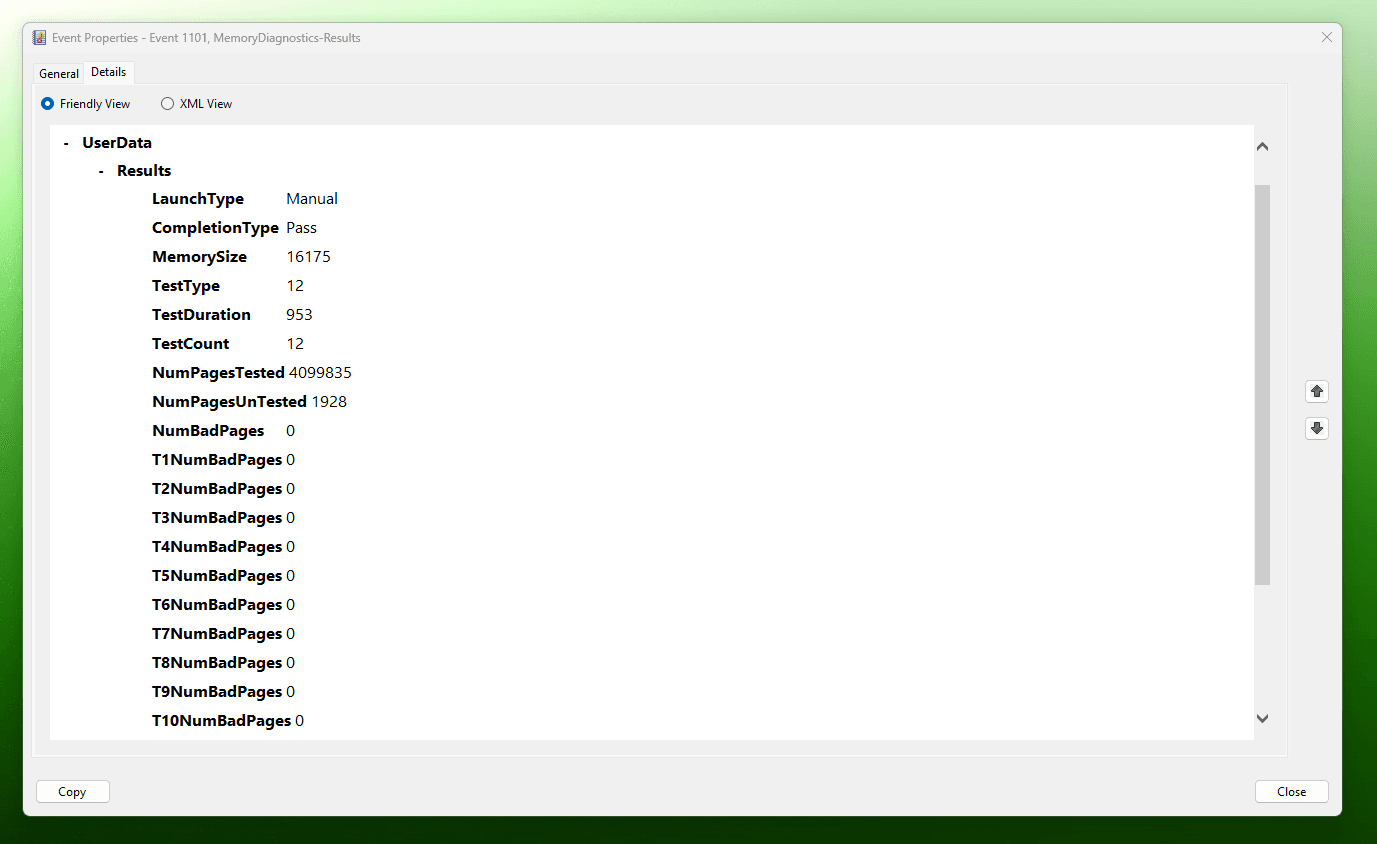
- Once the test is done, your system will restart automatically. If you want to check the results, just press Win + X >> Event Viewer >> Windows Logs >> System >> Windows Memory Diagnostics Results.
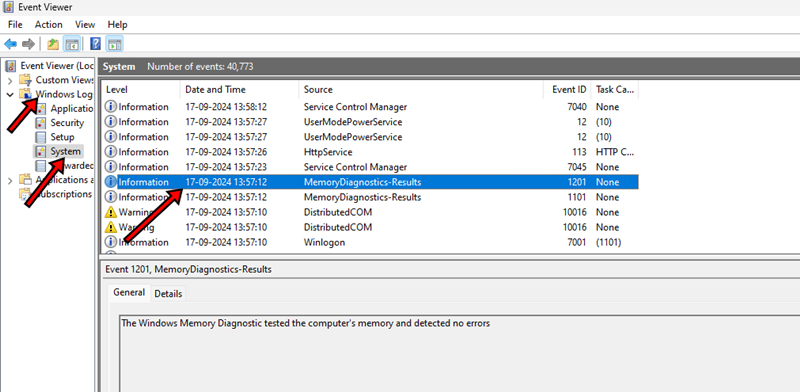
- The results will highlight the problems in the RAM if there are any.
Using the built-in memory diagnostics tool in macOS
- Restart your Mac and immediately hold down the
Dkey. - Follow the on-screen instructions to run the diagnostics.
You can also use the Memtest86+ software, which is also available for Linux operating systems.
8 Methods to Increase RAM/Memory Lifespan
1. Employ proper cooling
Proper cooling is essential for all your components. However, because high-frequency RAM modules can become very hot, it is necessary to ensure that good airflow reaches these modules. Ensure you use high-quality CPU and case fans; consider using liquid cooling if required.
Many RAM modules now come with passive heat sinks, which can dissipate heat more effectively in the case. Especially for the fast DRAM sticks, it is good to buy the heatsink variants of RAM.
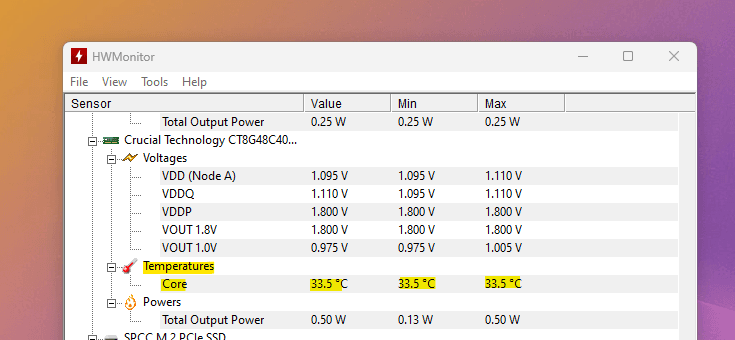
Under load, the RAM can easily reach 60°C. However, temperatures ranging from 30 to 50°C are considered normal for DDR4 RAM modules. The DDR5 RAM has much higher thermal tolerance, reaching up to 95°C. The average temperature under load is between 50 and 70°C. To check your RAM’s temperature, you can use the free tools like HWInfo and CPUID HWMonitor. If you notice the temperature rising above 60°C while performing everyday tasks, it may be a sign of overheating; in this case, you should take action.
2. Avoid Overclocking
RAM is rated for a specific speed, which is measured in MHz or GHz. Additionally, a particular voltage and timing are required for the RAM to function properly. When we overclock the RAM, we tweak these settings to achieve higher RAM speed. You can always perform safe overclocking, but sometimes, things can go wrong and result in excessive heat, and in some rare cases, permanent damage to the memory chips.
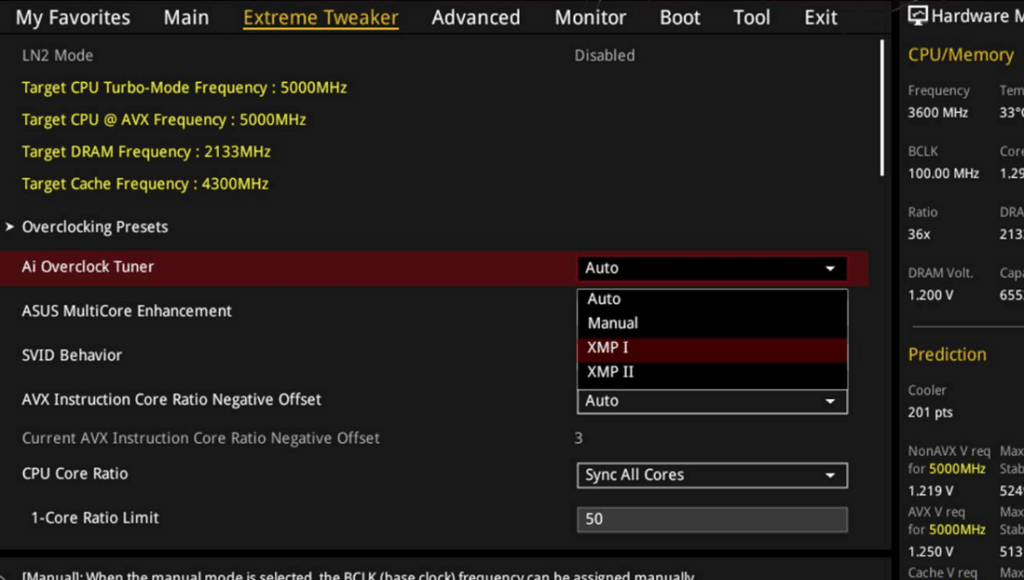
With modern motherboards, you’ll find built-in memory overclocking tools, such as Intel XMP and AMD EOCP profiles. These features enable users to utilize pre-configured overclock settings safely, allowing for overclocking of the RAM without manual adjustments.
Users can also manually adjust the RAM speed, voltage, and timings in the motherboard’s BIOS. This provides greater control over the settings but carries higher risks if not done carefully.
The key drawbacks of any type of RAM overclocking are increased heat, void warranty (some manufacturers), shortened lifespan, and BSOD Errors. It is best not to overclock your RAM if you don’t have arrangements for effective heat management. However, you can use the motherboard tools and gradually increase the settings. Keeping a constant eye on RAM performance and heat generation is essential. But, overall, if you want your RAM to last longer, it is best not to overclock it.
3. Use a good power supply
A power supply can play a significant role in extending your RAM’s lifespan. This is because the RAM modules are sensitive to voltage fluctuations. They are designed to operate within a specific voltage range (e.g., 1.2V for DDR4, 1.35V for DDR4 with XMP profiles). Unstable power supplies can induce electrical noise and interference, leading to data corruption and accelerated degradation.
A PSU with 80 PLUS certification (Bronze, Silver, Gold, or higher) is essential for the proper functioning of all computer components.
Although motherboards have VRMs to stabilize the power input to both RAM and CPUs, good power input to the VRMs is essential for their output as well. Some motherboards also come with Over-voltage and over-current protection. Investing in a good motherboard is also necessary for ensuring a proper power input to the RAM.
4. Keep RAM clean and dust-free
Dust buildup on the DRAM module can block the airflow and obstruct heat dissipation. This can increase the temperature and may also result in electrical shorts. Regularly clearing the RAM and the whole computer is a good thing. This is crucial, especially in desktop computer cases.
5. Reduce Memory Load
Overutilizing your RAM will put an extra burden, which increases read/write operations and, consequently, the temperature. Additionally, you can upgrade the RAM and add memory if you frequently run multiple apps simultaneously. In a nutshell, allowing more headroom to the memory will reduce the stress.
You can check the Activity Monitor or Task Manager to see which apps are consuming the most of your system’s memory. If any of these isn’t essential to you, it is better to uninstall it or close it whenever it is not required.
6. Regularly restart your computer
Using your computer for extended periods can also result in faster RAM degradation. Constant use can lead to memory leakage and unnecessary memory consumption. Restarting your laptop refreshes the memory and cleans all the temporary memory locations. In this way, you are freeing up space and increasing the lifespan of your RAM.
7. Install RAM in Matched Sets
This isn’t very important, but it can still ensure the proper working of multiple RAM sticks together. Using the same modules of RAM on a single motherboard will reduce the voltage and timing discrepancies. It is good to buy matched kits. Or, if you are upgrading the RAM, ensure that you match the size, speed, voltage, and latency numbers properly with the existing RAM module (s).
8. Take care of physical handling
RAM modules are relatively thin PCBs. A little extra pressure can easily bend it, especially when it is without any heatsink. Therefore, ensure that you remove and install them carefully. Also, when removing or installing, ensure that you do not expose them to electrostatic discharge. It is good to ground yourself properly before touching the RAM sticks. Anti-static wrist straps are pretty affordable.
Proper seating of RAM sticks is also significant. Improper seating can result in a poor connection, which can lead to stability issues, crashes, and bad power input to the RAM. When installing the RAM, make sure the memory sticks properly and click them into their dedicated slots. It must be locked in its place.
I hope this helps!