Affiliate Disclosure: This post may include affiliate links. If you click and make a purchase, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Over the years, I’ve worked with file compression software in everything from everyday file sharing to large-scale backups, software distribution, and long-term archival storage. It seems like a simple decision. Mostly, it starts with simple file zipping, but it quickly becomes a technical decision once performance, compression ratios, encryption, compatibility, and reliability matter.
Choosing the right file compression software depends on how you actually use it. Users dealing with documents, source code, or logs benefit from algorithms optimized for high compression ratios, while those handling media files often prioritize speed and format support over size reduction.
Compatibility is another important factor here. ZIP remains the most universally supported format, but modern formats such as 7z and zstd offer better efficiency when both ends of the workflow are under your control. Strong encryption and password protection are important priorities for some users. I have discussed data compression in this article. Also, I have made a data compression calculator, which is really popular among my readers.
In this guide, I’ll break down the best file compression software available in 2025 based on my own experience. The focus is on measurable performance, supported formats, update history, and practical trade-offs, so you can choose a tool that fits your workload. So, without any delays, let’s get started.
Honorable Mention: Windows Built-In File Compression
For most people with basic data-compression needs, the built-in file compression feature in Windows 10/11 is more than enough. Before looking at third-party tools, it’s worth noting Windows’ built-in file compression functionality. File Explorer supports creating and extracting ZIP archives natively, with no additional software required.
Right-click any file or folder, then choose Compress to. You can compress to a ZIP, 7z, or TAR File without using any third-party software. If you decide on Additional options, you can select different compression methods, including LZMA2 and Deflate. Also, you can choose from a range of compression levels.
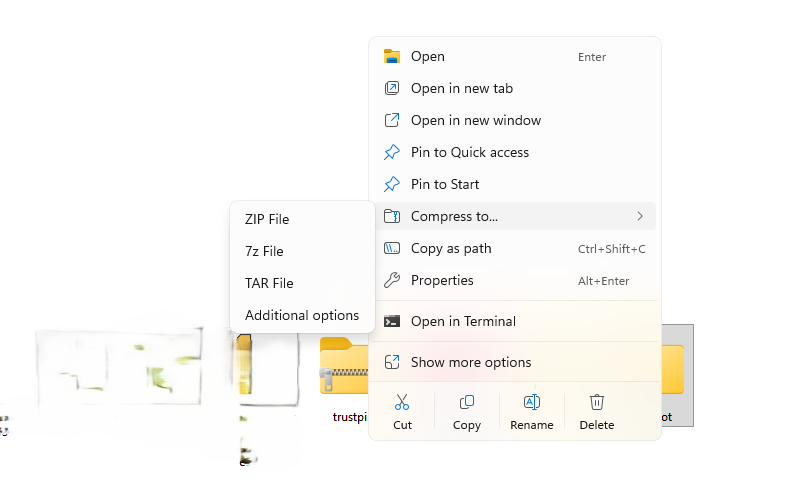

Built-in zip gets the job done for casual use. When you need heavier compression, password tricks, or batch automation, it’s time to grab one of the tools below.
1. 7-Zip (Best overall)

| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Excellent compression ratios with 7z (LZMA/LZMA2), especially for text and binaries | Default UI is dated and less intuitive than some commercial alternatives |
| Completely free and open-source with no feature restrictions | Cannot create RAR archives |
| Supports strong AES-256 encryption for files and filenames | 7z format is not universally supported by default on all systems |
| Handles very large archives and files without artificial limits | Cannot create RAR archives |
| Password Protection available |
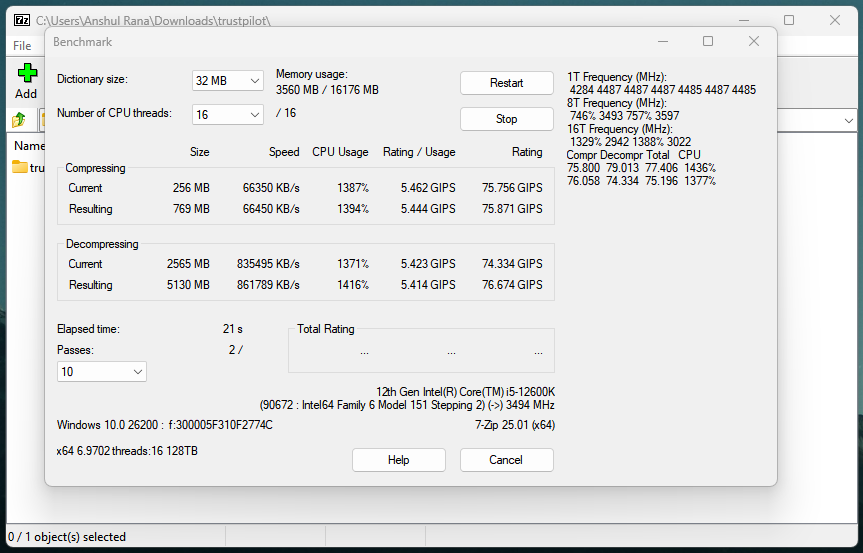
7-Zip is one of the most popular data compression software programs for Windows. Natively, it supports .7z compression using the LZMA and LZMA2 algorithms. I have used a lot, mainly because of its low system overhead and excellent performance. This software has put a strong emphasis on format flexibility and compression efficiency.
The LZMA2 compression algorithm, used in 7-Zip, is well optimized for multi-core processors. It leverages modern CPU parallelism, enabling stronger compression and larger dictionary sizes. In real-world scenarios involving mixed file sets, 7-Zip often produces noticeably smaller archives than ZIP, especially when pre-compressed media files do not dominate the dataset.
7-Zip isn’t limited to its native .7z format; it can create archives in 7z, ZIP, TAR, WIM, and several other formats, and extract from many more, including RAR, ISO, CAB, DMG, and various Linux archive types. Also, 7-Zip supports AES-256 encryption in 7z and ZIP formats, with the option to encrypt both file contents and filenames.
In my opinion, the primary and only trade-off lies in usability and convenience. The graphical interface is functional but dated, lacking some of the polish and workflow features found in commercial alternatives. But it does the job well for which it has been made.
2. WinRAR (Best for RAR workflows)
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Native support for RAR and RAR5 formats, widely used in professional and legacy workflows | Proprietary software requiring a paid license for continued use |
| Excellent archive recovery and repair features via recovery records | Compression ratios typically trail 7-Zip at maximum settings |
| Reliable handling of large archives and multi-part volumes | Windows-focused, with weaker native support on other platforms |
| AES-256 encryption with encrypted file headers for enhanced security |
Unlike 7-Zip, WinRAR is a proprietary file compression and archiving utility best known for its native RAR and RAR5 archive formats. It is widely preferred in professional, enterprise, and long-standing distribution workflows. The RAR5 compression algorithm is WinRAR’s standout feature. It features better performance and scalability compared to the earlier RAR versions. RAR5 is also well-optimized for multi-core processors, supporting a large dictionary size and handling big archives efficiently.
In terms of compression ratio, the RAR5 format is slightly behind 7-Zip at maximum settings. However, it has a higher compression speed when compared side by side to 7-Zip. One of WinRAR’s most substantial technical advantages is its focus on archive robustness and error recovery. You can use the Repair feature on any damaged archive, and the software will try to fix it for you. WinRAR is also known for handling split archives pretty well. This makes it an ideal choice for distributing large files in segmented parts.
You also get WinRAR encryption and security features, including AES-256 encryption for RAR and ZIP archives, secure password handling, and encrypted file headers to hide filenames. You can also scan your files for viruses on the go.
Regarding the format support, it can create RAR and ZIP archives and extract from many standard formats, including 7z, ISO, TAR, CAB, and legacy archive types. The user interface is quite good and modern. It will ask you to upgrade to a paid version many times. So, you will have to keep that in mind. I have been using WinRAR for years now, and I can attest to its stability and performance without a second thought.
3. WinZip (Most Features in paid version)
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Excellent ZIP compatibility for universal file sharing | Compression ratios are weaker than those of 7-Zip and WinRAR |
| Native GUI applications for both Windows and macOS | Subscription-based pricing model |
| Built-in cloud integrations (OneDrive, Google Drive, Dropbox, etc.) | ZIPX format offers limited real-world benefits |
| Fast compression suitable for frequent everyday use | |
| AES-256 encryption support | |
| Includes additional productivity features (PDF tools, file conversion) |
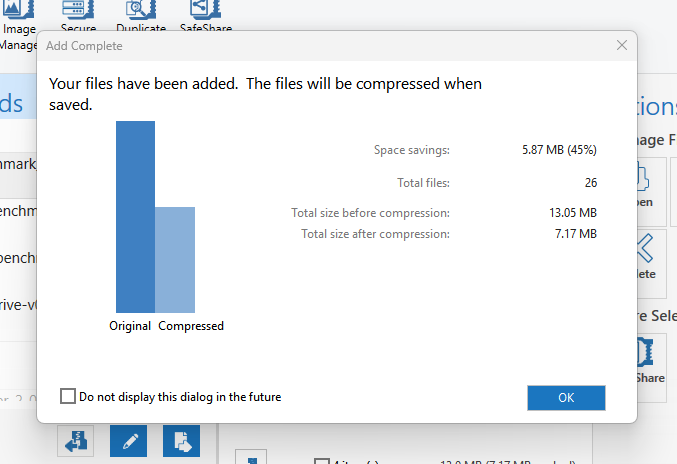
WinZip is one of the most popular programs used for file compression, encryption, archiving, and even file management. It is known for its user-friendly interface and cross-platform usability. It supports compression and extraction of a wide range of archive formats, including ZIP, ZIPX, 7Z, RAR (read-only), GZIP, TAR, ISO, and more, giving users broad compatibility with standard formats.
The software includes advanced file management features. Users can organize and browse files within archives, split large archives into smaller segments, and create self-extracting executable archives that recipients can open without installing additional software.
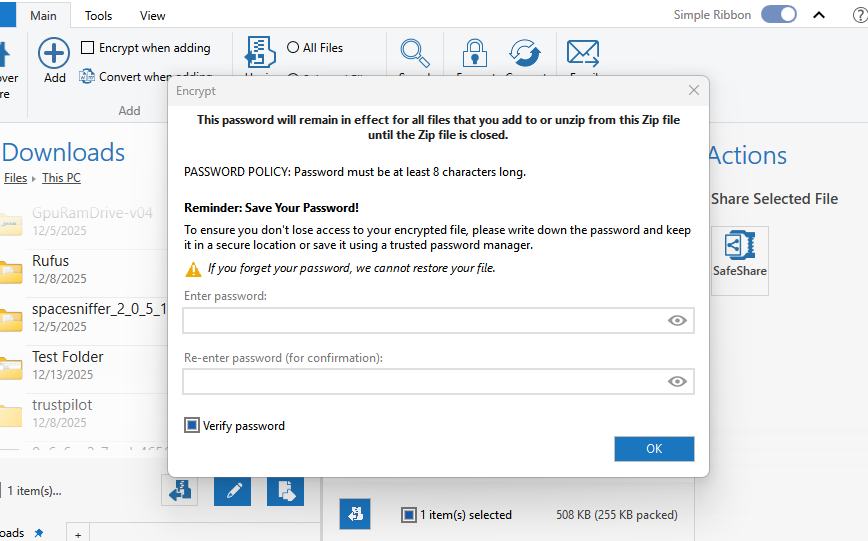
The software offers strong AES-based encryption (up to 256-bit), enabling users to protect sensitive files with passwords before compressing them. The latest version of WinZip also provides integration with popular cloud storage services such as Google Drive and Dropbox. I like WinZip mainly because it is designed to improve productivity and system organization.
However, I would recommend it only if its workload consists of heavy and professional file compression and extraction. For both regular and occasional use, it can be overkill for most users.
4. PeaZip (Best open-source)
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Completely free and open-source with no ads or trial limits. | Creating archives can be slower compared with some competitors. |
| Supports 200+ archive formats for extraction and many for compression. | Some advanced features (e.g., handling RAR creation) rely on external tools. |
| Strong security features, including advanced encryption and two-factor options. | Resource usage may be higher than that of ultra-light archivers. |
| Cross-platform support (Windows, Linux, macOS, BSD). |
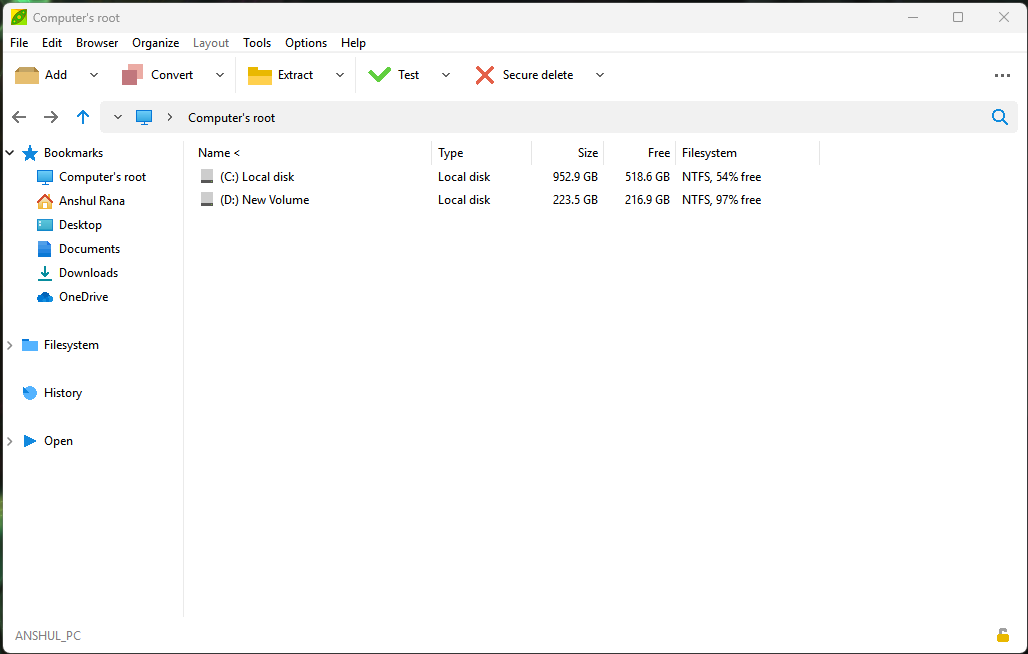
PeaZip is a free, open-source file archiver, compression tool, and file manager available for Windows, Linux, macOS, BSD, and ReactOS. It looks very much like Windows Explorer and is well integrated with it. It offers over 200 archive formats ,including mainstream ones like ZIP, 7Z, TAR, RAR, PEA, ARC, and ZIPX, along with less common formats like ZPAQ, PAQ/LPAQ, Brotli, Zstandard, and more.
One of PeaZip’s unique strengths is its native PEA archive format, which combines compression with flexible encryption, multi–volume spanning (splitting archives), integrity checking, and authenticated encryption. PeaZip supports AES-256 encryption for ZIP and 7Z, along with features like random password generation, secure file deletion, and hash calculation.
PeaZip is not only a file archiver but a suite of different software. It can perform tasks such as splitting/joining files, batch renaming, converting between archive formats, and editing files within archives without extracting them. This makes the program super helpful, but complex at the same time. You get no ads and a feature-rich program for free.
PeaZip is an excellent choice for those looking for a free, fully-featured program. However, the native compression method is PEA format, which uses a deflate-based algorithm. So, if you are good with a less popular native compression, PeaZip is definitely a great option.
5. Bandizip (Best for speed + modern Windows GUI)


| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Fast performance with multi-core support. | The free version may include advertisements, and some advanced tools require a paid upgrade. |
| Can create ZIP, 7Z, TAR, ISO, and extract from many others, including RAR. | Decompression speed is average |
| User-friendly interface | Niche formats or advanced compression tweaks may be less robust than tools like 7-Zip or WinRAR. |
| AES-256 encryption | macOS support lags slightly behind Windows |
| Smart extraction and Unicode support make workflows smoother, |
I was a heavy user of Bandizip because it supported the most popular compression methods and its archive repair feature. I might have switched to much simpler tools now, but Bandizip was once my favorite.
Bandizip has separate free and paid options. Bandizip is widely appreciated for its high performance, broad format support, and straightforward interface. The key selling point is performance: it uses multi-core processing to accelerate compression and decompression, enabling faster file handling than many competitors. The impact can be huge when we work with modern multi-core CPUs.
Bandizip also includes security features, such as AES-256 encryption for password-protecting archives. In the paid edition, you get features like antimalware scanning, password management, archive repair, and image previews without extraction. Bandizip is primarily developed for Windows, though there is a separate macOS version with similar core functionality







I’ve installed PeaZip before; its interface is very similar to Windows File Explorer, making it easy to use. It’s quite convenient for decompressing, encrypting, and extracting files, and the fact that it’s ad-free and open-source is a huge plus. It has many features but isn’t difficult to use; it’s perfectly adequate for everyday tasks.