Solid State Drives (SSDs) in recent years have become the default choice for laptops and computers. It offers blazing fast speed compared to traditional HDDs, along with making sure that it is energy efficient and durable at the same time.
We can also not deny the fact that nothing in the world is everlasting. While SSDs are more reliable than ever, they still have limitations in the number of write cycles they can perform. It simply means the lifespan of an SSD can be affected by how the system manages the read/write operations.
Fortunately, Windows takes care of quite a few things behind the scenes. If you are a Windows user, you should be aware that there are many built-in features in the Windows operating system that are designed to reduce stress on SSDs. The best part is you don’t need to be an expert to use them. It handles everything, from automated cleanup to more elegant file handling – if you know where to look for them.
In this article, we will discuss 6 hidden features that are present in Windows and that most of us never come across.
1. Storage Sense
Storage Sense is a Windows-provided feature that monitors your system’s temporary files, recycle bin contents, and leftover updates. It automatically removes all the junk files and temp data that is not required. It also monitors your system for the Delivery Optimization cache (used when updating or installing apps). Storage sense, by automatically performing these tasks, reduces unnecessary writes to the SSD, eventually extending its usable life.
How to enable it?
- Open Settings
- Go to System -> Storage
- Click on Storage Sense
- Toggle it ON
2. TRIM Command
One of the most important features for SSD health is TRIM. In SSDs, unlike HDDs, data can’t be overwritten in place, instead, the memory cells are first erased. This amplifies the writing scenario, also known as write amplification. It slows down the performance and wears out the drive over time.
The TRIM command in the operating system tells the SSD which block of data is no longer in use after a file deletion. Instead of waiting for the block to be overwritten, the SSD controller marks those blocks as reusable.
TRIM reduces any chance of unnecessary operations erasing the data that is not required beforehand.
How to check if TRIM is enabled?
Most of the operating systems, including Windows, have TRIM enabled by default. You can verify it by using the following method.
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator (Important)
- Type the following command and press enter:
fsutil behavior query DisableDeleteNotify
If the result is DisableDeleteNotify = 0
It does mean that TRIM is enabled. If it says 1, TRIM is disabled.
Here is how you can enable TRIM if it is disabled.
3. NTFS Compression (Selective Use)
The idea of compression might sound illogical, but NTFS compression can help increase the drive’s lifespan if used selectively. The idea is simple. Reducing the file size will also reduce the amount of data required to be written on the SSD, enabling the drive to last longer.
NTFS file compression reduces files on the disk, but at the same time, the compression process adds a slight tension to the CPU, a very negligible overhead. The key can be compressing the files that are not used very frequently, such as older project branches, watched movies, etc.
How to apply compression:
- Right-click on the folder you want to compress.
- Click on properties
- Click Advanced
- Check “Compress contents to save disk space”
- Click OK, then Apply
4. Scheduled SSD Optimization
In SSDs, unlike HDDs, the Windows running optimization that you see is nothing but the new replacement method of traditional defragmentation. These are TRIM and retrim operations that are actually beneficial for solid-state drives.
In SSD schedule optimization, the SSD clears out the blocks that are marked as deleted and makes them available for future writes, keeping the performance consistent.
You can check the ongoing process by following the steps provided below.
- Press Windows + S and type “Defragment and Optimize Drives” in the search bar
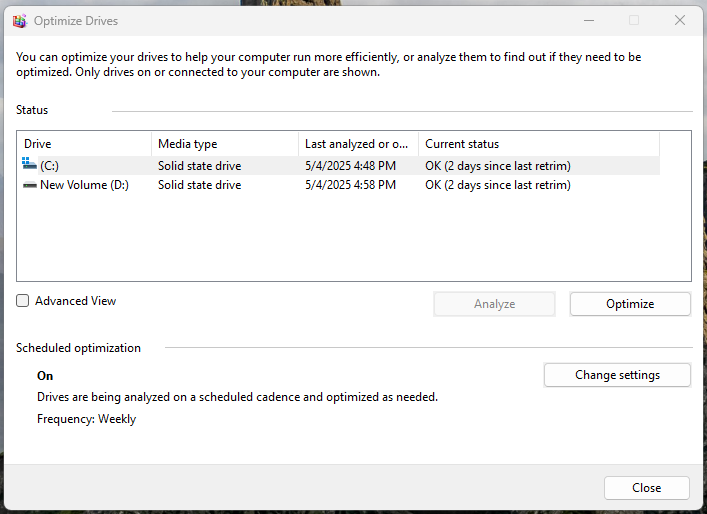
- Select the SSD
- You will see that its media type is “Solid State Drive” and the optimization involves retrim and not defrag.
- If you want to optimize manually, you can click the “Optimize” button, permissible only to administrators.
- You can also schedule optimization by clicking on the “Change settings” button
5. Hibernate and Fast Startup Settings
Hibernation is a great feature for fast startup, but when enabled on a system consisting SSD, it can be a not-so-good idea to perform it frequently, as it can increase the number of unnecessary write operations.
You can read the following article to understand how hibernation is never a good measure for a system with SSDs.
Steps to disable hibernation:
If you don’t use hibernation very frequently, it’s okay.
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator
- Type powercfg /hibernate off
- Press Enter
6. Reserved Storage
In the recent versions of Windows 10 (version 1903 and above) and Windows 11, Microsoft has incorporated a behind-the-scenes feature known as reserved storage. Many users might overlook it, but it plays a very significant role in protecting the lifespan of your SSD.
Reserved Storage improves the lifespan of the SSD by allocating a fixed portion of your SSD (typically 7 GB) for wear-leveling tasks such as system updates, temporary files, and caches. By moving these operations to reserved blocks, the operating system avoids this volatility from spreading across the drive, reducing the maintenance cost.
Conclusion
SSDs are blazing-fast, but everything comes with a price – write endurance. Fortunately, Windows includes many built-in features and tools designed to maximize the lifespan of SSDs without compromising performance. From storage sense to enabling TRIM to disabling hibernation, these small, quick tools can make a measurable difference. Taking advantage of these features makes sure that your SSD stays fast, reliable, and healthy throughout its life.