Affiliate Disclosure: This post may include affiliate links. If you click and make a purchase, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
The WD Black SN8100 is the fastest consumer Gen 5.0 SSD available. There are numerous competitions involved, with the Samsung 9100 Pro being the most notable one. The Crucial T705 is also in the competition, and we will reveal which one is the best for you, in case you are confused. The T705 cannot match the SN8100 in performance. Even the T710, which is significantly faster than the T705, was unable to beat the SN8100. However, I have been receiving numerous messages about this comparison, so I will compare both here.
I understand the confusion.
WD Black SN8100 targets the enthusiasts, while Crucial T705 is also a high-end drive. However, there is a price difference. The T705 generally saves you $10 to $20 on the 1TB variant, and up to $30 on the 2TB variant. The price difference is even bigger in the 4TB version. Therefore, the question of performance-to-price ratio arises for this amount. Is the extra money for the SN8100 worth it?
I am going to clear things up for you. But let me say upfront. The T705 is more than enough for most computers and laptops. However, SN8100 is the best of the best; you can equip your computer with it, and it comes with its benefits. We will see them later in the benchmark comparisons. But first, let’s compare the theoretical specifications.

Specifications Comparison
| Specification | WD Black SN8100 | Crucial T705 |
|---|---|---|
| PCIe Generation/NVMe Version | PCIe Gen 5.0 x4/ NVMe 2.0 | PCIe Gen 5.0 x4/ NVMe 2.0 |
| Release Date | Feb 20th, 2024 | Feb 20th, 2024 |
| Capacities | 1TB, 2TB, 4TB, 8TB | 1TB, 2TB, 4TB |
| NAND Flash | Kioxia BiCS8 TLC (218-layer) | Micron B58R FortisFlash TLC (232-layer) |
| Sequential Read Speed | 1TB: 14,900 MB/s 2TB: 14,900 MB/s 4TB: 14,900 MB/s | 1TB: 13,600 MB/s 2TB: 14,500 MB/s 4TB: 14,100 MB/s |
| Sequential Write Speed | 1TB: 11,000 MB/s 2TB: 14,000 MB/s 4TB: 14,000 MB/s | 1TB: 10,200 MB/s 2TB: 12,700 MB/s 4TB: 12,600 MB/s |
| Random Read Speed | 1TB: 1,600K IOPS 2TB: 2,300K IOPS 4TB: 2,300K IOPS | 1TB: 1,400K IOPS 2TB: 1,550K IOPS 4TB: 1,500K IOPS |
| Random Write Speed | 1TB: 2,400K IOPS 2TB: 2,400K IOPS 4TB: 2,400K IOPS | 1TB: 1,750K IOPS 2TB: 1,550K IOPS 4TB: 1,500K IOPS |
| DRAM | DDR4 | LPDDR4 |
| Controller | Silicon Motion SM2508 | Phison PS5026-E26 |
Surprisingly, both WD Black SN8100 and Crucial T705 were launched on the same day in February 2024, representing the cutting edge of PCIe Gen 5.0 NVMe 2.0 drives. However, their specs reveal some interesting trade-offs.
The SN8100 is well optimized for maximum performance of PCIe 5.0 generation across capacities, with consistently higher sequential read speeds (up to 14,900 MB/s) and notably stronger random read/write IOPS compared to the T705. The Crucial T705, while slightly behind in raw numbers, still delivers excellent speeds (up to 14,500 MB/s reads and 12,700 MB/s writes), and its Micron 232-layer NAND could potentially offer efficiency or endurance advantages over WD’s Kioxia 218-layer design. On the DRAM front, WD opts for standard DDR4, while Crucial uses LPDDR4, suggesting a focus on power efficiency. Controller choice also diverges: WD’s Silicon Motion SM2508 vs. Crucial’s Phison E26, both well-regarded but with different firmware tuning philosophies. In short, the WD Black SN8100 appears to be the raw performance champion. At the same time, the Crucial T705 may appeal to those who prioritize a balanced design, efficiency, and proven support from the Phison ecosystem.
Benchmark Scores Comparison
All benchmark scores are collected from the same internet sources for proper comparison. All of them are for 2TB variants of both drives. Let’s compare them all and see which one offers the best benefits.
PCMark 10 Benchmark Scores
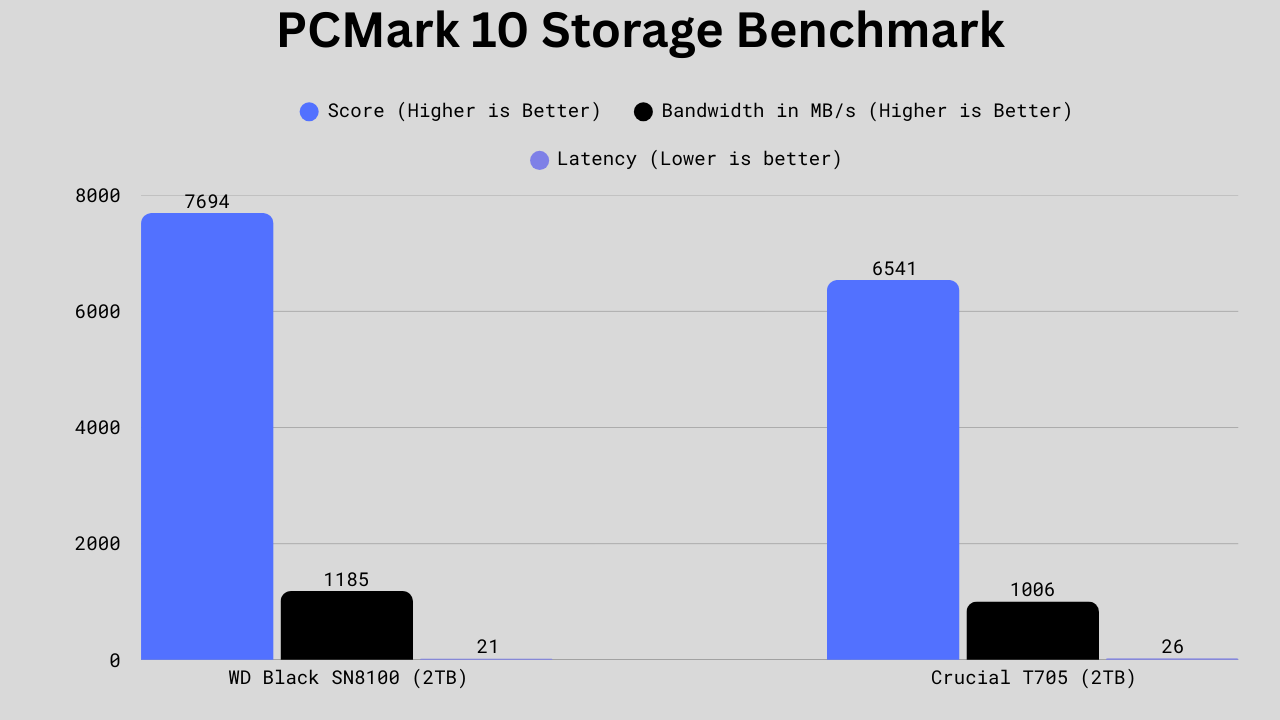
The WD Black SN8100 outperforms the Crucial T705 across the board, scoring approximately 17.6% higher overall (7694 vs. 6541), offering roughly 17.8% more bandwidth (1185 MB/s vs. 1006 MB/s), and delivering around 19% lower latency (21.0 µs vs. 26.0 µs). In real-life use, this translates to slightly quicker OS/Software load times, faster handling of large files for video editing or content creation, and snappier responsiveness in multitasking or professional workloads that depend on low latency. For everyday users, the difference will likely be minor, as both drives are high-speed. However, for enthusiasts and professionals, the SN8100 has a definite edge.
3DMark Storage Benchmark for Gamers
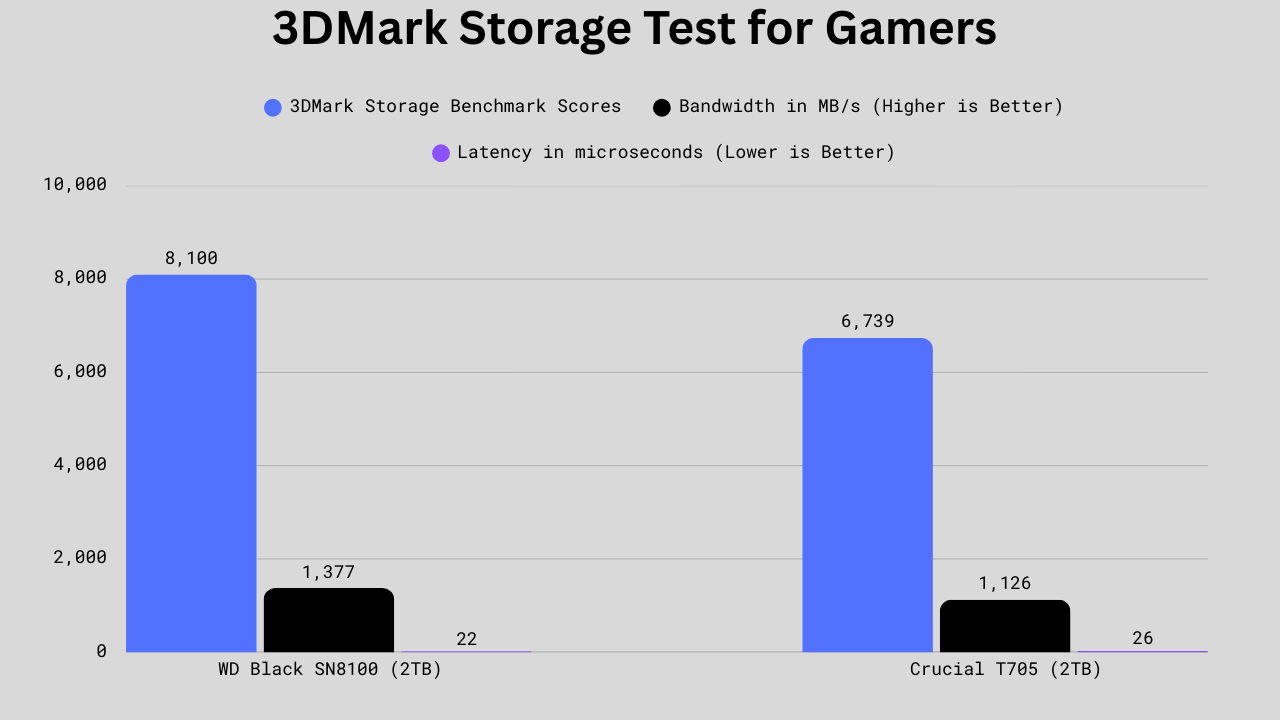
The WD Black SN8100 again takes the lead over the Crucial T705, scoring about 20% higher overall in 3DMark’s storage benchmark (8100 vs 6739), offering roughly 22% more bandwidth (1377 MB/s vs 1126 MB/s), and achieving around 15% lower latency (22 µs vs 26 µs). This means the WD drive will feel more responsive in demanding tasks, from loading significant game levels faster to handling big project files more smoothly in creative workloads. The WD Black’s advantage becomes more noticeable for gamers, streamers, power users, and professionals who frequently deal with heavy workloads or multitasking.
CrystalDiskMark Sequential Read/Write Benchmark
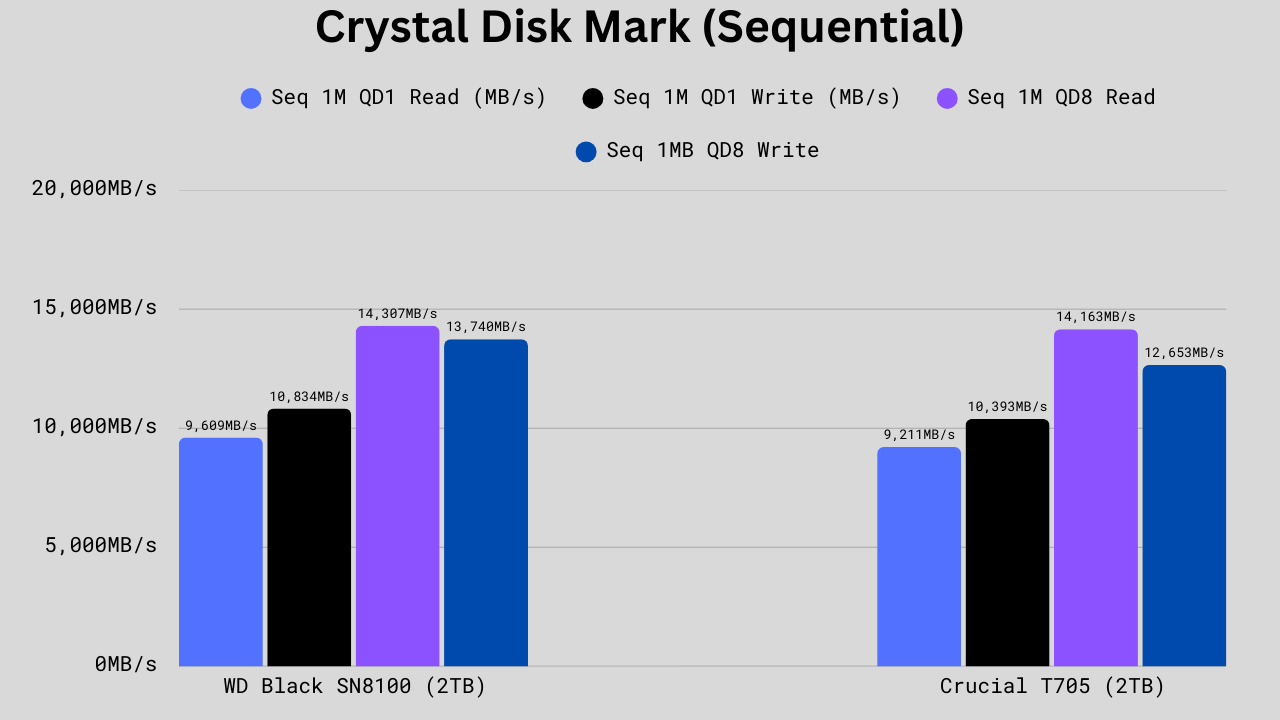
WD Black SN8100 beats the Crucial T705 in every category in the sequential read/write benchmarks. It’s about 4% faster in QD1 reads (9609 MB/s vs 9211 MB/s), roughly 4% faster in QD1 writes (10,834 MB/s vs 10,393 MB/s), just 1% faster in QD8 reads (14,307 MB/s vs 14,163 MB/s), and around 9% faster in QD8 writes (13,740 MB/s vs 12,653 MB/s). In real-world use, the small gains in QD1 (single-queue) speeds translate to slightly snappier everyday responsiveness. At the same time, the larger advantage in QD8 writes means the WD Black will handle sustained, high-volume transfers, such as large video exports, backups, or game installations.
CrystalDiskMark Random Read/Write Benchmark
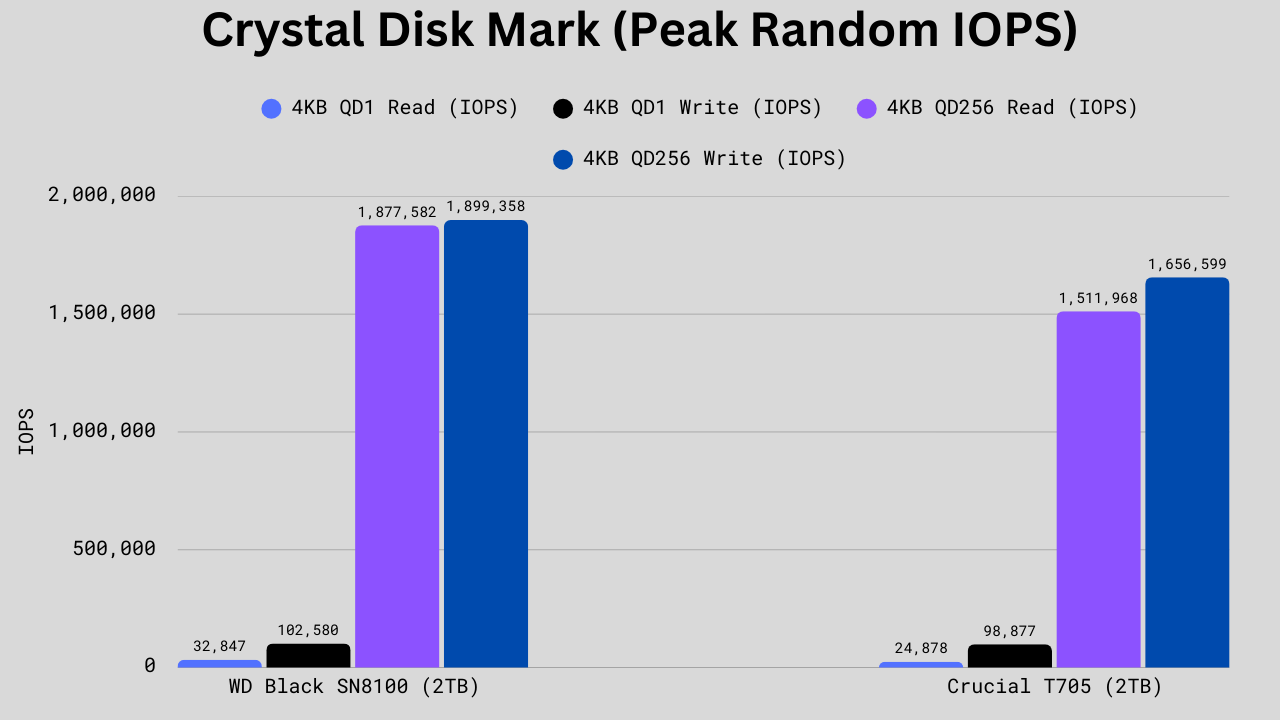
In random 4K performance, the WD Black SN8100 shows clear advantages over the Crucial T705. QD1 reads are about 32% faster (32,847 vs 24,878 IOPS), QD1 writes are slightly higher at ~4% (102,580 vs 98,877 IOPS), while at high queue depths (QD256) the WD leads by ~24% in reads (1,877,582 vs 1,511,968 IOPS) and ~15% in writes (1,899,358 vs 1,656,599 IOPS). These differences matter most in scenarios where numerous small files are accessed simultaneously, such as booting Windows, loading apps, running databases, or multitasking under heavy workloads, where the WD Black will feel more responsive and consistent. For general use, both drives are fast enough that casual users won’t notice a significant difference.
Transfer Rate Benchmark
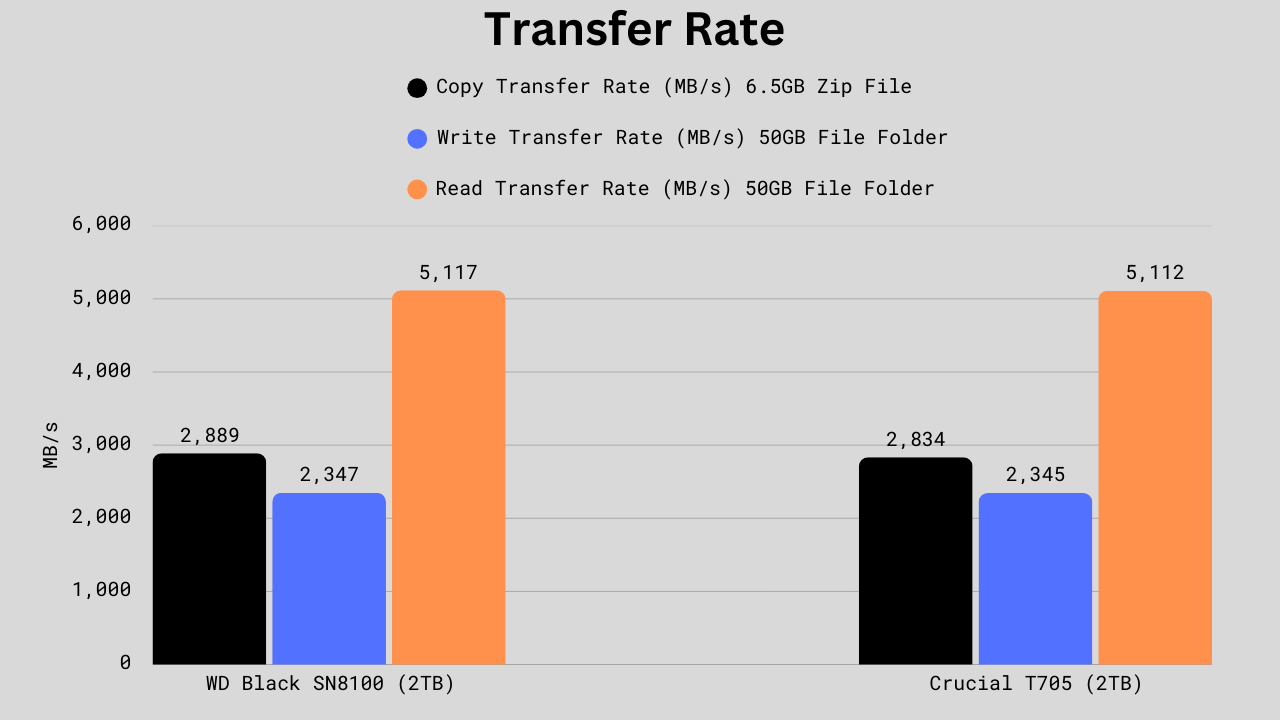
WD is just 2% faster in copying a 6.5GB zip file (2889 vs 2834 MB/s), essentially identical in 50GB write speed (2347 vs 2345 MB/s), and only 0.1% faster in 50GB read speed (5117 vs 5112 MB/s). In practice, these margins are so small they’d be imperceptible to an end user. Both drives will copy, read, and write large folders at virtually the same blistering pace. This means that for heavy workloads, such as moving large game files, raw video footage, or backups, either drive will perform equally well, with no meaningful advantage to either side.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
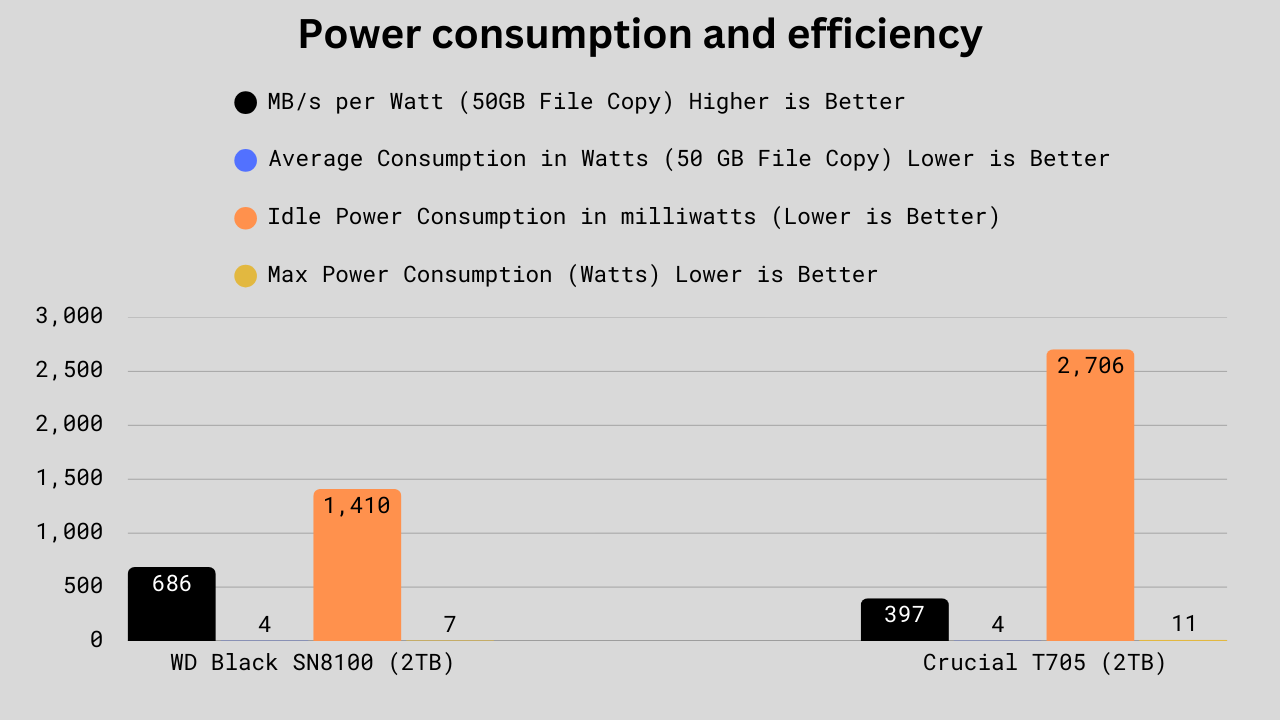
In terms of efficiency and power, the WD Black SN8100 is ahead, delivering approximately 73% more performance per watt in a 50GB file copy (686 vs 397 MB/s per watt), while drawing the same average power during the transfer (4W each). Its idle power use is also significantly lower, at 1.41 kW vs 2.706 kW (nearly half), and its maximum power draw under heavy load is 35% lower (7.45W vs 11.46W). For real-world usage, this means the WD Black runs cooler, uses less energy, and is better suited for laptops or systems where heat and power efficiency are essential.
Tech Specs
| Specification | WD Black SN8100 | Crucial T705 |
|---|---|---|
| Controller | Silicon Motion SM2508 | Phison’s PS5026-E26 |
| Controller Architecture | ARM 32-bit Cortex-R8 + ARM 32-bit Cortex-M0 | ARM 32-bit Cortex-R5 + AndesCore 32-bit N25F RISC-V (5-Core) |
| DRAM Specifications | DDR4 DRAM 1TB: 1×1024 MB 2TB: 1×2048 MB 4TB: 1x 4096 MB | Micron’s LPDDR4 DRAM 1TB: 1×1024 MB 2TB: 1×2048 MB 4TB: 1x 4096 MB |
| SLC Write Cache | 1TB: approx. – 2TB: approx. 600 GB 4TB: approx. – | 1TB: approx. 110 GB (dynamic only) 2TB: approx. 220 GB (dynamic only) 4TB: approx. 440 GB (dynamic only) |
| NAND Flash | Kioxia BiCS8 TLC NAND | Micron’s B58R FortisFlash TLC |
| Topology | 218-Layers | 232-Layers |
| NAND speed | 3600 MT/s | 2400 MT/s |
| Read Time (tR)/Program Time (tProg) | 40 µs/unknown | 61 µs/600 µs |
| Die Read Speed | Unknown | 1574 MB/s |
| Die Write Speed | 205 MB/s | 160 MB/s |
| Encryption | AES-256, TCG Opal | AES-256, TCG Opal |
| Power Loss Protection | No | No |
| SMART/TRIM/PS5 Support | Yes/Yes/Yes | Yes/Yes/Yes |
The WD Black SN8100 places a strong emphasis on raw NAND performance, pairing its Silicon Motion SM2508 controller with Kioxia’s 218-layer BiCS8 TLC NAND, which operates at a blistering 3600 MT/s. This helps explain its industry-leading sequential speeds and high random IOPS. The faster NAND also brings shorter read latency (40 µs vs. 61 µs) and stronger per-die write throughput (205 MB/s vs. 160 MB/s) compared to Crucial’s drive.
The Crucial T705, powered by Phison’s flagship E26 controller with a more complex hybrid core design (ARM Cortex-R5 + RISC-V Andes N25F), appears to be tuned for a balanced and scalable performance profile rather than chasing maximum NAND speed. While its Micron 232-layer B58R NAND is slower on paper (with a 2400 MT/s interface), its larger dynamic SLC cache (up to 440 GB on 4TB models) ensures smooth performance even under heavy write bursts, which benefits creators handling large sequential workloads.
Both drives support AES-256 encryption, TCG Opal, SMART/TRIM, and PS5 compatibility; however, neither includes power-loss protection, a feature typically reserved for enterprise SSDs. DRAM capacity is identical, scaling appropriately with storage size, although Crucial’s use of LPDDR4 offers a slightly lower power draw compared to WD’s standard DDR4.
TBW, DWPD, MTBF, and Warranty
| Specificiation | WD Black SN8100 | Crucial T705 |
|---|---|---|
| TBW (Terabytes Written) | 1TB: 600 TBW 2TB: 1200 TBW 4TB: 2400 TBW | 1TB: 600 TBW 2TB: 1200 TBW 4TB: 2400 TBW |
| DWPD (Drive Writes per Day) | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| MTBF (Mean Time Between Failure) | 1.8 Million Hours | 1.5 Million Hours |
| Warranty | 5 Years Limited | 5 Years Limited |
The TBW and DWPD numbers are the same in both SSDs across capacities. However, the SN8100 comes with a higher Mean Time Between Failure.
Price Difference
The SN8100 is generally on the expensive side. The 2TB variant of SN8100, for example, is available for 229$ by the time I am writing this article. The T705 2TB can be purchased for 199$. The price difference is almost similar in other variants as well. However, it keeps changing, and I advise you to check before you make your purchase.
Conclusion
For performance enthusiasts and those seeking the best SSD performance on the market, the SN8100 will deliver an exceptional experience. However, it is clearly overkill for most systems and most use cases. The SN8100 is ideal for high-end workstation users who need to run virtual machines, train AI/ML models, or perform tasks with massive random I/O. Data-intensive creatives, such as video editors, VFX designers, and 3D modelers, can also benefit from SN8100. For others, the SN8100 is clearly a waste of resources until they have a free budget to spend.
The T705 offers a perfect balance between performance and price. Its performance is at the top of the charts in the Gen 5.0 category. However, when we compare it, the SN8100 outperforms it significantly. Still, it is great for content creators, gamers, and even high-performance everyday users. It will save you some money, which you can spend on other components.
I hope this helps!