M.2 SATA vs 2.5 SATA SSD: What is the Real Difference?
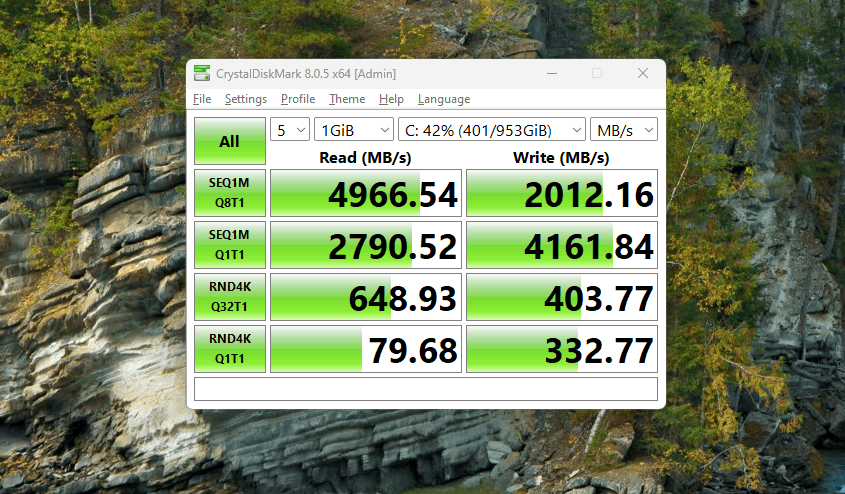
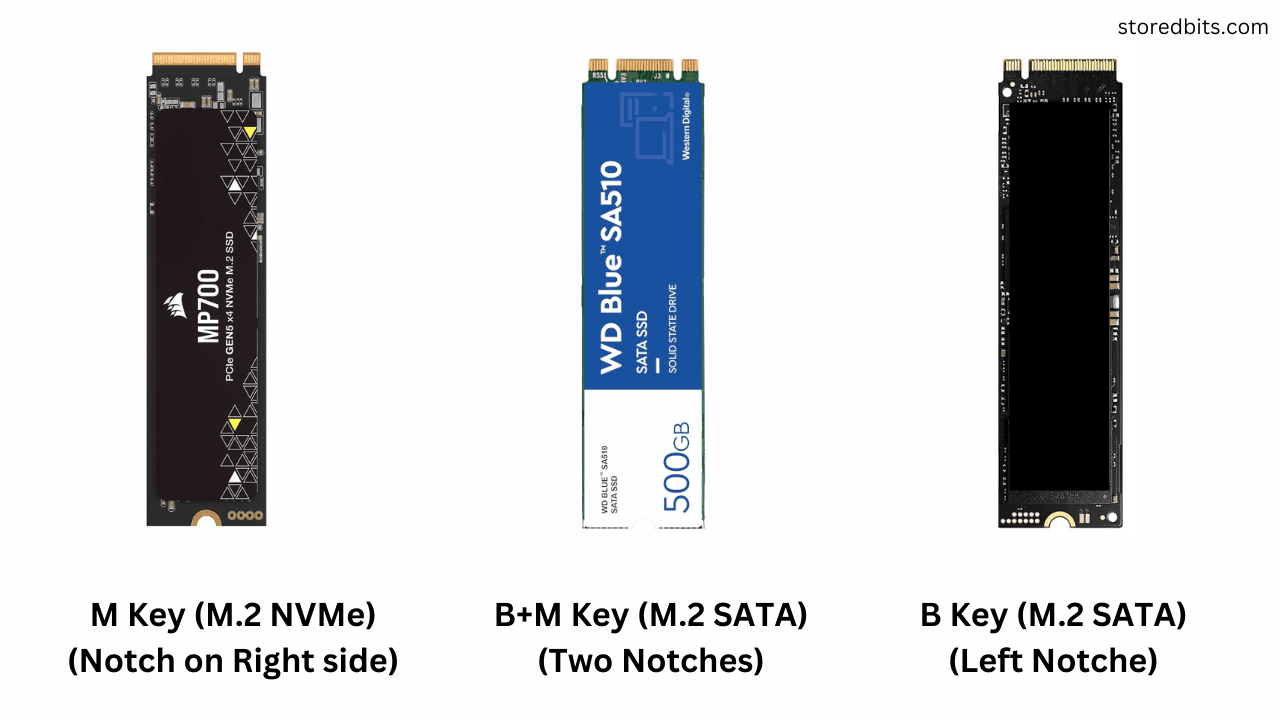
M.2 SATA and 2.5 SATA SSDs are the same in terms of performance. However, there is a size difference between the both. Because the M.2 SATA SSDs look like M.2 NVMe SSDs, people get confused between them. A 2.5-inch SSD is called 2.5″ because of the drive’s physical size, specifically its width. The 2.5 inch […]