Affiliate Disclosure: This post may include affiliate links. If you click and make a purchase, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
SSD is one of the easiest upgrades for your computer when you know the right drive to choose. However, it can be a complex thing when you don’t know what to look for. Things can become even worse when you don’t even know the terminology. So, here is my beginner’s answer to another popular question: M.2 vs. NVMe. Although this may not be the right question to ask, I will attempt to clear up all the confusion.
M.2 and NVMe are often used together to indicate fast drives. However, these two are entirely different things. M.2 determines the physical properties of components in electronics. NVMe can be described as a set of rules that determine how an SSD interacts and transfers data with the CPU. It utilizes the basic application of maximizing the NAND Flash memory used in SSDs. However, the drive must utilize the PCIe lanes for the primary interaction.
M.2 allowed the SSDs to become way smaller than the hard drives and SATA SSDs. On the other hand, NVMe-enabled SSDs can achieve impressive speeds, reaching read/write rates of 14GB/s on our computers.
What is M.2?
M.2 is an SSD form factor under which there are two main types of SSDs, i.e., M.2 SATA and M.2 NVMe. The form factor defines the size, shape, and other physical aspects of devices and components in electronics.
Any SSD sized under the M.2 specifications is referred to as an M.2 SSD. Now, it could either be NVMe or SATA. So, M.2 is just a size specification made for solid-state drives. It is also known as the Next Generation Form Factor (NGFF).
The M.2 drives come in five different sizes, which are as follows.
| M.2 Size (Form Factor) | Width (mm) | Length (mm) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2230 | 22 | 30 | Used in ultra-compact devices like tablets and some laptops. |
| 2242 | 22 | 42 | Generally found in small laptops, mobile devices and mini-PCs. |
| 2260 | 22 | 60 | Less common, used in mid-size devices where a longer drive can be accommodated. |
| 2280 | 22 | 80 | The most common size for desktops, laptops, and servers. |
| 22100 | 22 | 100 | Used in specialized applications where space is available for a longer drive. |
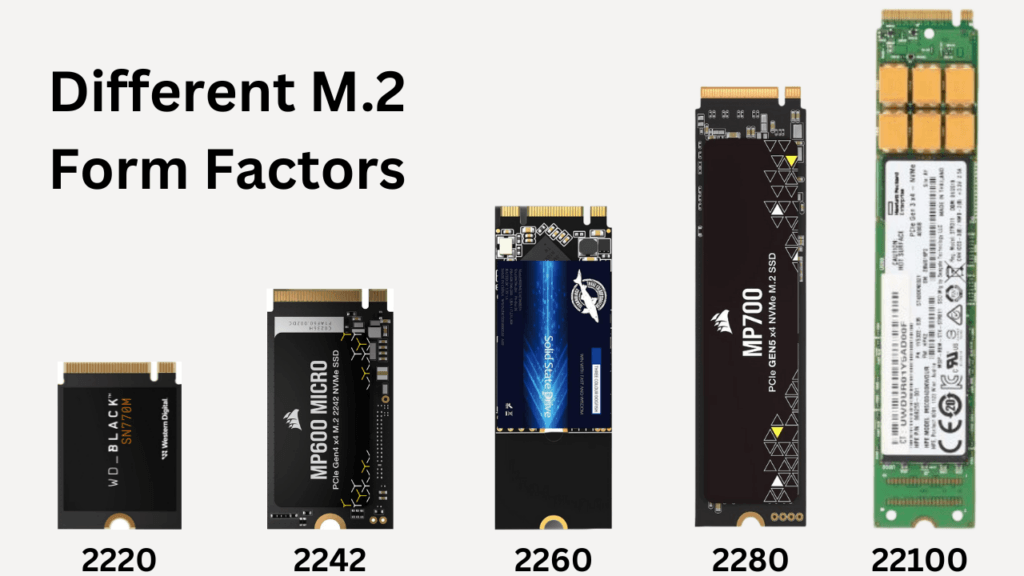
Therefore, M.2 drives will be available in any of these five sizes. However, M.2 never defines their speed, latency, compatibility, price, power consumption, and applications. M.2 just says that your drive is going to be one of these five dimensions.
With the NVMe drives, you often see this form factor written. Most commonly, you will find drives in the 2280 form factor. For example, the Samsung 990 Pro will have 2280 written on its sales page. So, the 2280 defines its dimensions.
Differences in Notches and Compatibility
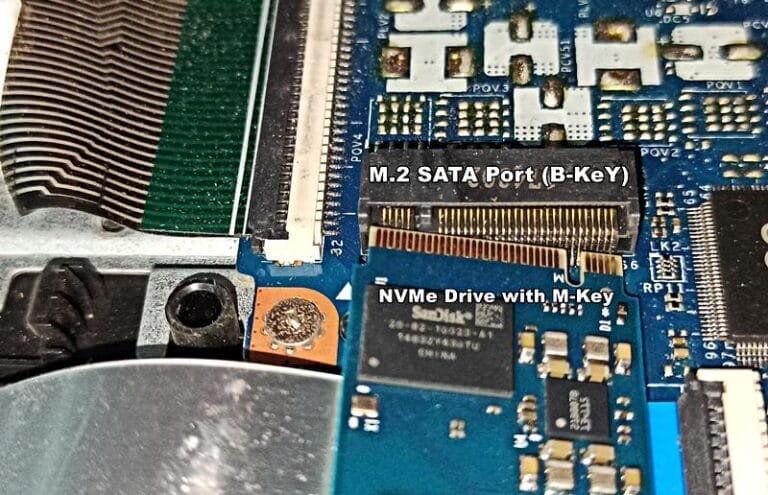
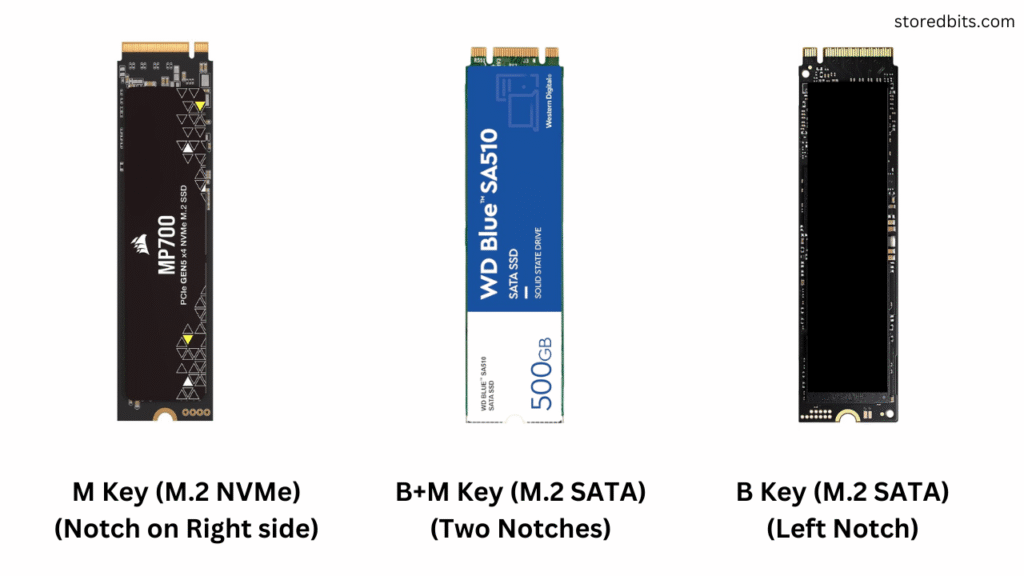
Although the M.2 drives share the exact dimensions, they can have different connector types. This is important to mention because it determines the physical and software compatibility of a drive on a laptop/desktop.
There are three types of keyings on these drives, i.e., M-Key, B-Key, and M+B Key. M-Key is a standard notch for M.32 NVMe drives, while the B-Key and B+M Key connectors are for M.2 SATA drives. We can install B-Key M.2 SATA drives in both M.2 SATA and M.2 NVMe slots. But, the M.2 NVMe drive will not work on M.2 SATA-only ports.
What is NVMe?
When you connect an SSD to your system, it is connected to the central system through an interface. For NVMe drives, it is the PCIe interface, and for SATA SSDs, it is the SATA interface. But what is NVMe?
NVMe is a protocol that determines how the data is transferred between the CPU and SSD. Again, the lanes will be PCIe (generally 4 lanes). The connection is the same, just like other components, such as graphics cards, but NVMe allows the host system to utilize parallelism in SSDs. The NVMe protocol is specifically designed to minimize latency as much as possible in PCIe drives.
NVMe can work with M.2, U.2 and even PCIe SSD cards. The condition is that the SSD must have PCIe lanes allocated to it. NVMe is also an interface, but it is a logical one. In other words, it works on the software level. When you have a drive connected through the PCIe lanes on your system, you unlock a higher bandwidth than the SATA interface. With the help of NVMe, this high PCIe bandwidth is combined with parallel operations to achieve a very high transfer rate.
Without the NVMe, the system must use the AHCI protocol, which is designed for SATA drives. The AHCI protocol cannot operate at a bandwidth of 6 Gbps (600 MB/s in real-world applications). It has a single command queue with a maximum of 32 commands at a time.
The maximum command queues with the NVMe protocol are 65,535. Each of these queues can handle 65,536 commands. So, if you multiply these numbers, you have around 4 billion commands at once. NVMe leverages parallelism, a key capability in electronics that enables multiple tasks to be performed simultaneously. SSDs use NAND flash, which is inherently capable of parallelism; however, the NVMe protocol is how we take advantage of it.
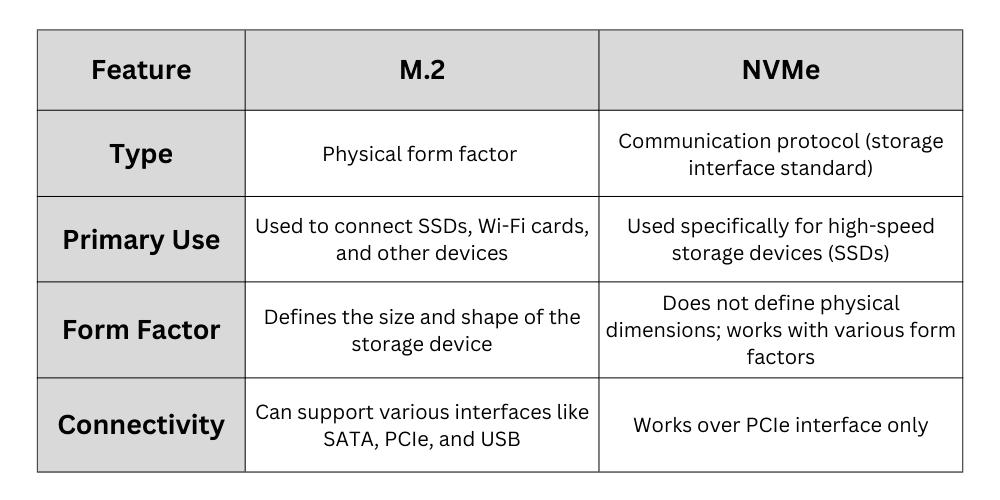
Talking about the difference between M.2 and NVMe
Now, you have a basic understanding of both concepts. Let me clarify it for you again.
M.2 just indicates that an SSD is going to be of a specific size. There are five form factors that we discussed above. M.2 drives can’t have dimensions other than these five. SSDs can be categorized into various groups, including PCIe generation, brand, and price. But, form factor is one of the main parameters.
NVMe, on the other hand, is a set of rules for data transmission. It is implemented in your drive’s firmware and also in the operating system through the NVMe drivers. It ensures that the NAND Flash memory on your SSD is utilized to its full potential. It leverages the multiple cores of your CPU, faster PCIe lanes, SSD controller, and NAND flash to achieve the SSD speeds we see today.
Can NVMe work without M.2?
NVMe SSDs rely on PCIe lanes for communication with the host system. Therefore, as long as the drive is connected through the PCIe lanes, NVMe will function properly. Even if you are connecting your NVMe device to the PCIe slot using a PCIe riser or extension cable, NVMe will still perform its job. However, because M.2 provides a direct and nearby connection to the CPU through the PCIe lanes, it will give you some advantages in latency and overall performance.
Can there be M.2 without NVMe and vice versa?
Yes, M.2 ports are used for M.2 SATA SSDs and some other expansion cards like Wi-Fi with different form factors. It is simply a form factor that can be used with many M.2 drives. It isn’t limited just to NVMe drives.
Also, NVMe can be there without M.2 in U.2, PCIe Add-in cards, BGA (In Notebooks), EDSFF (E1.S, E1.L, E3), and CFExpress. In the consumer environment, we mainly see M.2 and Add-In cards using NVMe. M.2 is the most popular implementation of NVMe drives in client SSDs.
FAQs about M.2 vs NVMe drives?
Can we compare M.2 and NVMe drives?
By comparing M.2 and NVMe, we are comparing the size of a drive to its way of communicating with the system. So, this comparison isn’t appropriate.
What are the types of M.2 drives?
M.2 SATA and M.2 PCIe NVMe drives are the most popular applications of M.2. However, you can see Wi-Fi cards and other expansion cards in the M.2 form factor.
If NVMe is for M.2 PCIe drives, what is for M.2 SATA drives?
Just like NVMe is a transfer protocol (set of rules) for M.2 PCIe drives. M.2 SATA drives use the AHCI protocol. NVMe is designed to maximize the utilization of parallelism in NAND Flash memory, along with the higher bandwidth of PCIe lanes compared to SATA lanes.
What are other SSD form factors besides M.2?
SATA SSDs also come in a 2.5″ form factor that replicates the dimensions of standard 2.5″ hard drives. Also, there are PCIe Add-in Cards, U.2 SSDs, mSATA SSDs, and ball grid SSDs that connect directly to the motherboard.
Ask questions in the comments!