Affiliate Disclosure: This post may include affiliate links. If you click and make a purchase, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Crucial T710 can be considered the big brother of the T705, with better performance to offer. Both are Gen 5.0 x4 NVMe SSDs with the TLC NAND flash, although the flash configurations are different. Both drives come in 1TB, 2TB, and 4TB variants. Both have their own DRAM, but they use different controllers.
The main difference is in the performance. The T710 offers sequential read/write speeds of up to 14,500 MB/s and 13,800 MB/s, respectively. The T705, on the other hand, promises sequential read speeds of 14,100 MB/s and write speeds of 12,600 MB/s.
The NAND flash in the T710 is Micron’s B68S FortisFlash with 276 layers. Its raw speed is 3600 MT/s. The T705 is equipped with a slightly slower B58R FortisFlash with 232 layers. It has a raw throughput of 2400 MT/s. The controllers are also different: the T710 uses Silicon Motion SM2508 at 1250 MHz, while the Phison E26 powers the T705 at 1000 MHz.
Overall, the T710 is going to win in terms of performance. However, if we look at the price-per-GB for average or even high-end users, the T705 is a better value. In fact, both drives are focused on high-end users, but it is up to you whether you want the best-of-the-best from Gen 5.0 NVMe or you settle for a little less. No matter what you decide to choose, this guide is going to help you understand the difference properly.
Theoretical Specifications
| Specification | Crucial T705 | Crucial T710 |
|---|---|---|
| PCIe Generation/NVMe Version | PCIe Gen 5.0 x4/ NVMe 2.0 | PCIe Gen 5.0 x4/ NVMe 2.0 |
| Release Date | Feb 20th, 2024 | May 19th, 2025 |
| Capacities | 1TB, 2TB, 4TB | 1TB, 2TB, 4TB |
| Sequential Read Speed | 1TB: 13,600 MB/s 2TB: 14,500 MB/s 4TB: 14,100 MB/s | 1TB: 14,900 MB/s 2TB: 14,500 MB/s 4TB: 14,500 MB/s |
| Sequential Write Speed | 1TB: 10,200 MB/s 2TB: 12,700 MB/s 4TB: 12,600 MB/s | 1TB: 13,700 MB/s 2TB: 13,800 MB/s 4TB: 13,800 MB/s |
| Random Read Speed | 1TB: 1,400K IOPS 2TB: 1,550K IOPS 4TB: 1,500K IOPS | 1TB: 1,800K IOPS 2TB: 2,200K IOPS 4TB: 2,200K IOPS |
| Random Write Speed | 1TB: 1,750K IOPS 2TB: 1,550K IOPS 4TB: 1,500K IOPS | 1TB: 2,200K IOPS 2TB: 2,300K IOPS 4TB: 2,300K IOPS |
| NAND Flash | Micron’s B58R FortisFlash TLC | Micron B68S FortisFlash TLC |
| DRAM | Yes | Yes |
| Controller | Phison E26 | Silicon Motion SM2508 |
| Price | 1TB starting at $154.99 | 1TB starting at $179.99 |
The Crucial T710 has higher theoretical sequential and random read/write speed numbers. But, how well they will actually serve us will be seen in the benchmark scores comparison.
Benchmark Scores Comparison
These benchmark scores are for the 2TB variants of both drives.
PCMark 10 Scores Comparison
PCMark 10 is a full-fledged software suite for testing a storage drive’s capabilities in real-world usage scenarios. It runs numerous tests, including file copying and running Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign, among others. It also does some game loading, file moving, and saving. Many productivity and creative software are loaded to check your SSD’s capabilities in the real world. You can choose a quick or full storage test as per your desire. But, at the end, you get results with the PCMark 10 score (higher is better), bandwidth (higher is better), and latency (lower is better).
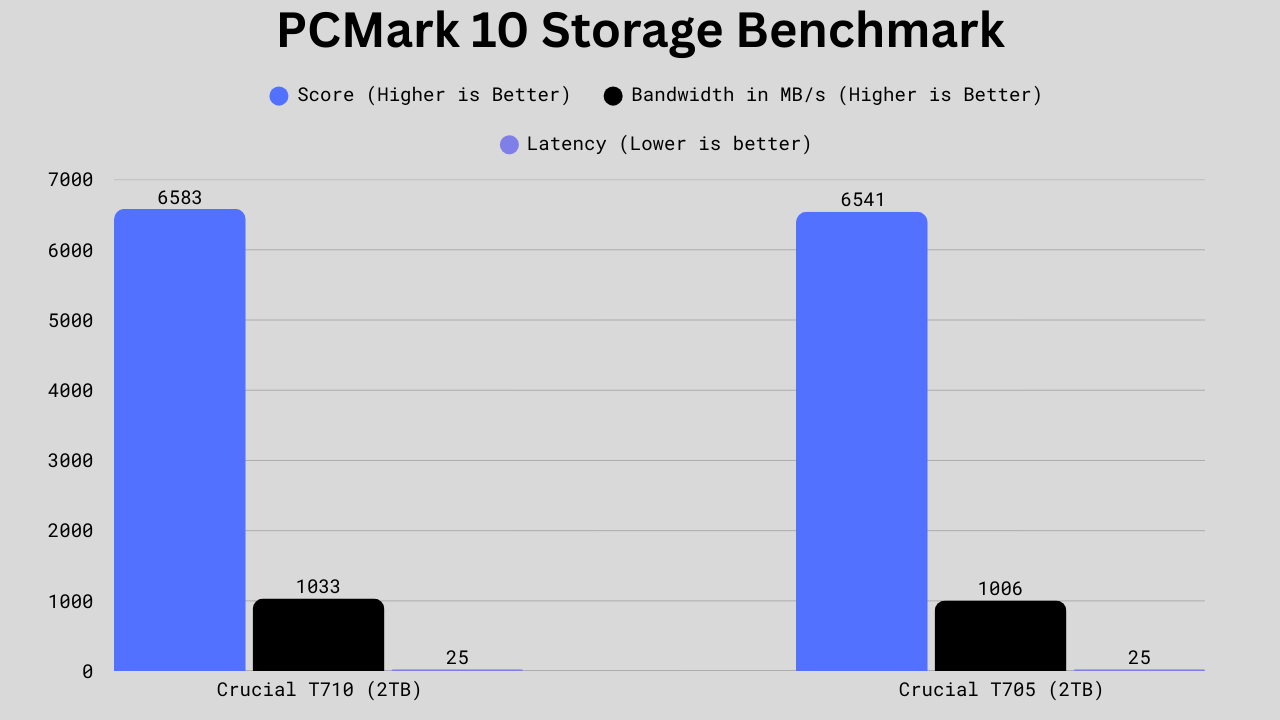
In the PCMark 10 benchmark, the Crucial T710 pulls slightly ahead of the T705, though the differences remain modest. The T710 scores 6,583 points, just 42 points (0.6%) higher than the T705’s 6,541. Bandwidth also favors the T710 at 1,033 MB/s versus 1,006 MB/s, giving it about a 2.7% advantage in throughput. Latency is identical at 25.0 microseconds for both drives, showing no measurable difference in responsiveness. These results suggest the T710 has an edge in efficiency and bandwidth over the T705, though the performance gap is minimal and unlikely to be noticeable in day-to-day workloads.
3DMark Storage Test for Gamers
The 3DMark Storage Test for gamers takes your SSD through numerous gaming and 3D-related tasks. The test mainly included game loading, installing, moving files, saving files, and streaming. It also provides the results, including the 3DMark score, bandwidth, and latency.
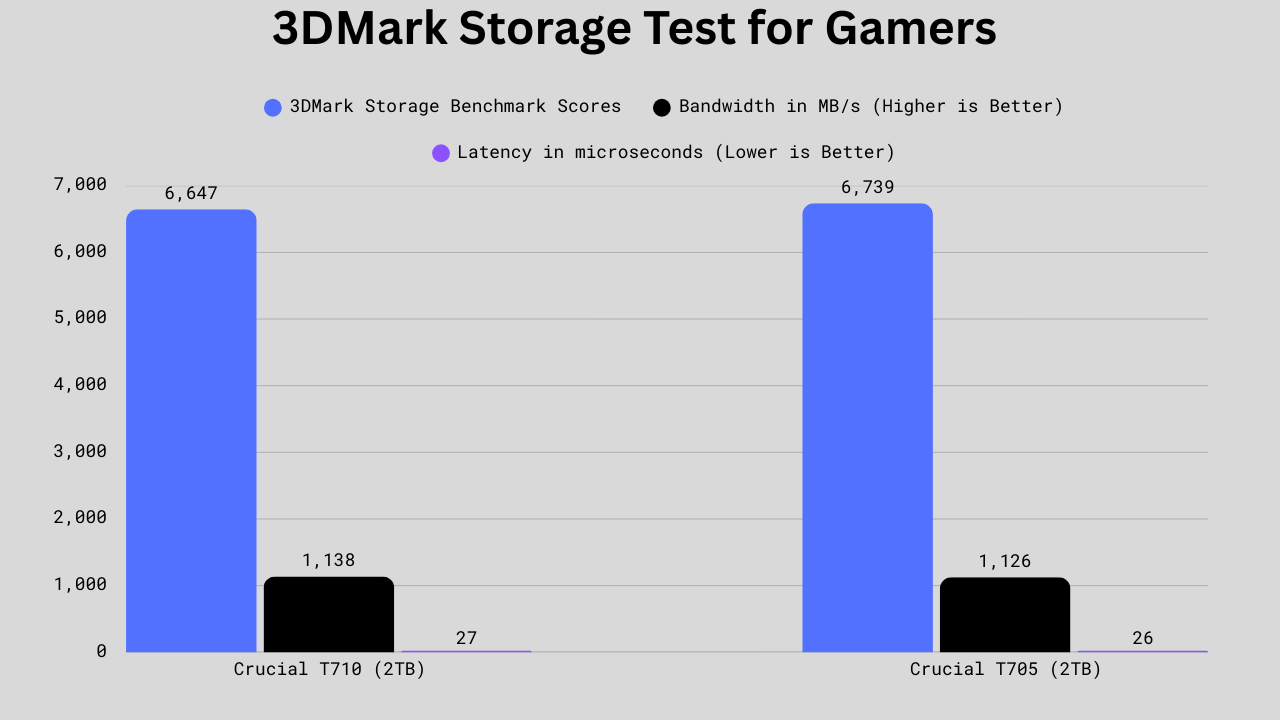
The T705 leads slightly in the overall score at 6,739 compared to the T710’s 6,647, a gap of just 92 points or about 1.4% higher. In bandwidth, the T705 again edges ahead at 1,126 MB/s versus the T710’s 1,138 MB/s, meaning the T710 is technically 1% slower in raw throughput. Latency shows the closest result, with the T705 at 26 microseconds and the T710 at 27 microseconds, a negligible 3.8% difference. Overall, the T705 is surprisingly faster in the 3DMark benchmarks. So, we can surely expect a little better results in gaming and 3D-related works.
CrystalDiskMark Sequential Read/Write Performance Comparison
The CrystalDiskMark sequential benchmark measures how fast the drive can read and write large blocks of data stored in contiguous locations. Sequential data is accessed in order and generally represents bigger files like video files, game installations, ISOs, etc.
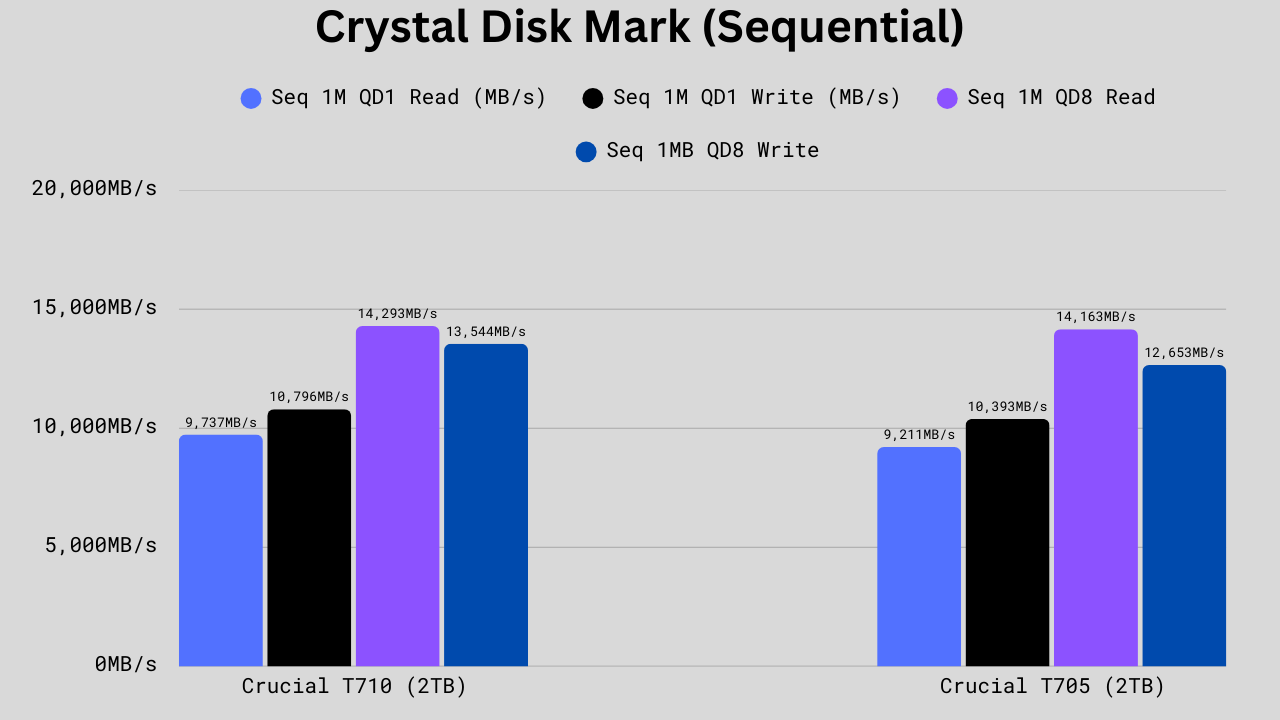
Looking at sequential performance, the Crucial T710 shows consistent gains over the T705 across nearly every metric. At QD1 read, the T710 reaches 9,737 MB/s, which is about 5.7% faster than the T705’s 9,211 MB/s. In QD1 write, the T710 delivers 10,796 MB/s compared to 10,393 MB/s on the T705, a 3.9% improvement. For QD8 read, the difference is minimal, with the T710 at 14,293 MB/s versus the T705’s 14,163 MB/s. However, in QD8 write, the T710 shows its largest gain, reaching 13,544 MB/s, which is 7.0% higher than the T705’s 12,653 MB/s. Overall, these results highlight that while both drives are high-speed, the T710 consistently edges out the T705, especially in write-heavy workloads.
CrystalDiskMark Random Read/Write Performance Comparison
The CDM Random read/write benchmark tests the drive performance when fetching small blocks of data from random locations. This test is typically done with the 4KB block sizes. This benchmark encompasses tasks such as OS booting, database lookups, and loading game assets, among others.
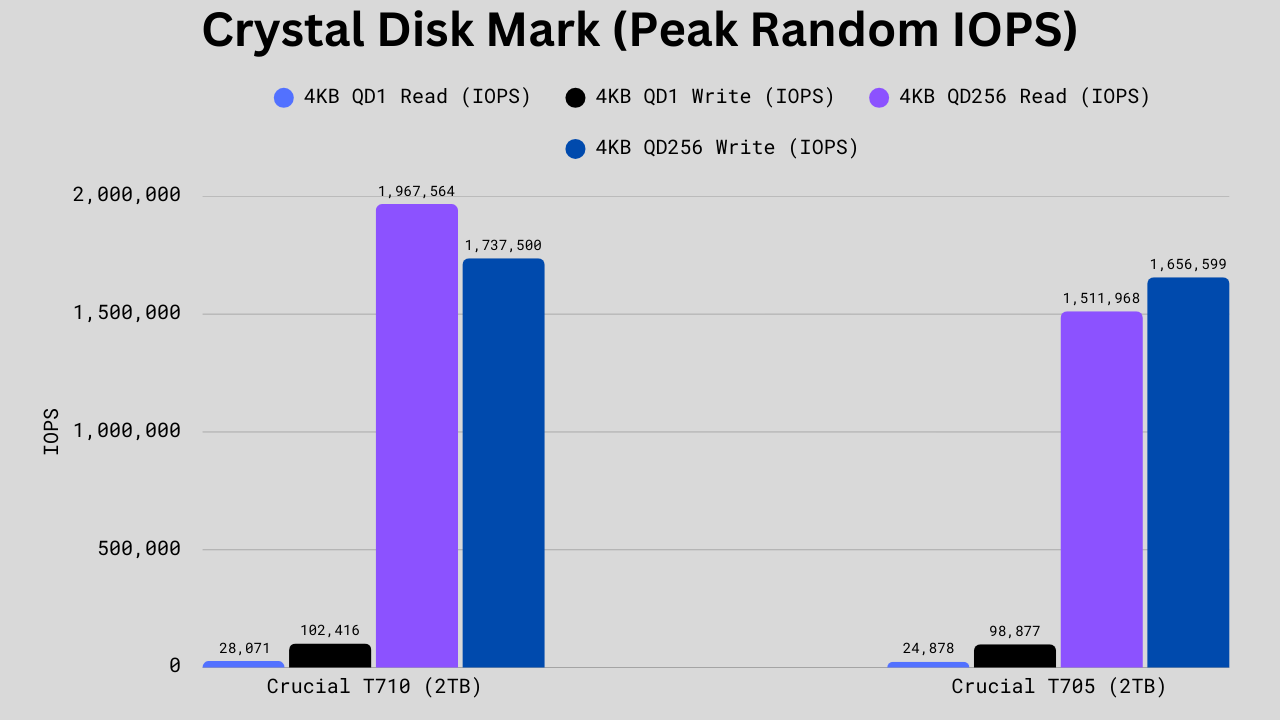
In random 4K performance, the Crucial T710 again beats the T705, especially at higher queue depths. At QD1 read, the T710 achieves 28,071 IOPS, about 12.8% higher than the T705’s 24,878 IOPS. For QD1 write, the difference is minor but still in favor of the T710, with 102,416 IOPS versus 98,877 IOPS, a 3.6% gain. The gap widens significantly at QD256 read, where the T710 hits 1,967,564 IOPS, which is an impressive 30% boost over the T705’s 1,511,968 IOPS. In QD256 write, the T710 also maintains an edge at 1,737,500 IOPS compared to 1,656,599, a more modest but still meaningful 4.9% advantage. These results suggest that the T710 offers noticeably stronger random performance, particularly in heavy multi-threaded or server-like workloads.
Transfer Rate Comparison
This test is done to check your drive’s capabilities for moving raw data from one place to another. We have used different types of data, like Zip files and 50GB file folders.
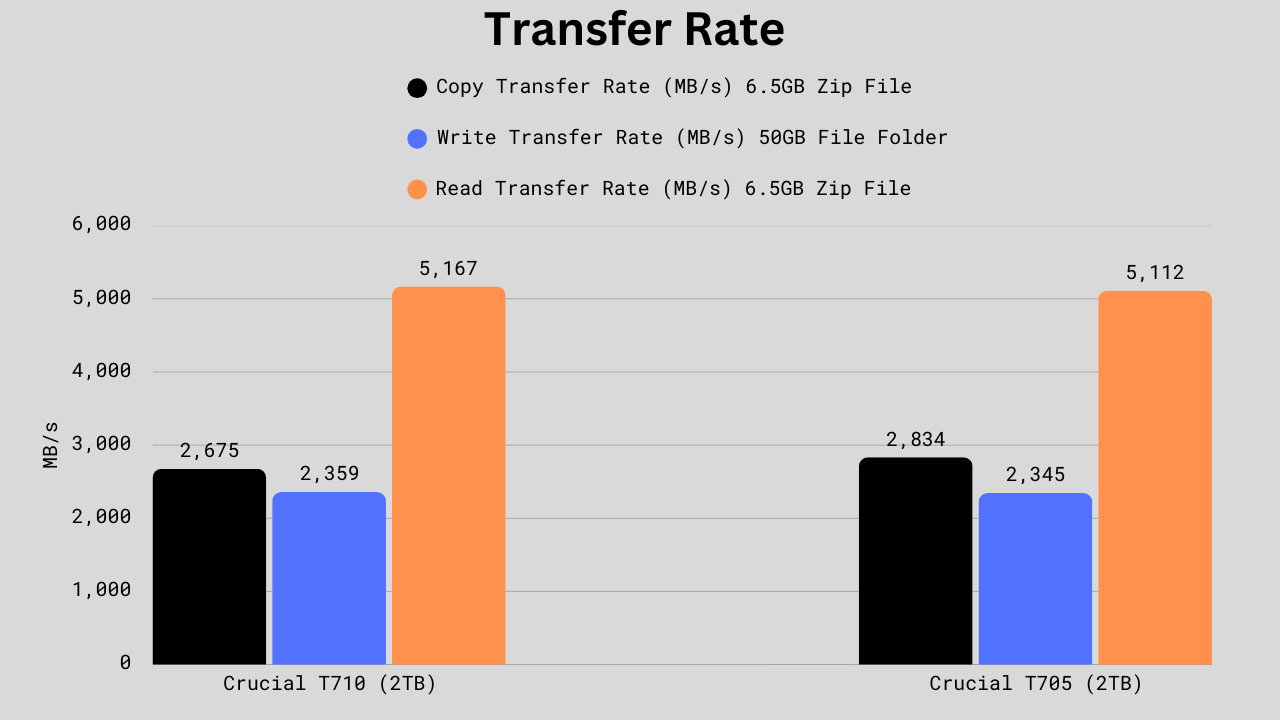
For the 6.5GB zip file copy test, the T705 reaches 2,834 MB/s, about 5.9% faster than the T710’s 2,675 MB/s. In the 50GB file folder write test, performance is nearly identical, with the T710 at 2,359 MB/s and the T705 at 2,345 MB/s, a negligible 0.6% difference in favor of the newer drive. For the 6.5GB zip file read test, the T710 reclaims the lead at 5,167 MB/s versus 5,112 MB/s, a 1.1% improvement. Overall, these results show that while the T710 generally edges ahead in read and large write operations, the T705 still holds a slight advantage in smaller compressed file transfers.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
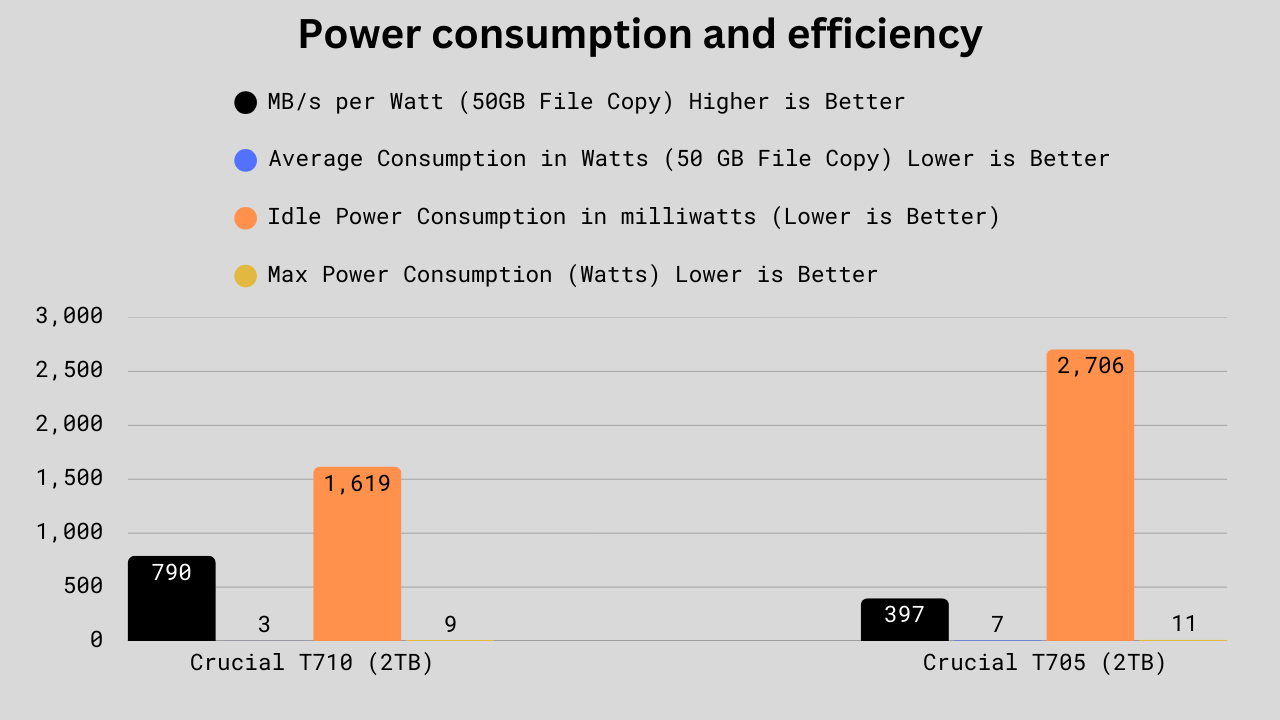
In terms of power efficiency, the Crucial T710 shows dramatic improvements over the T705. For the 50GB file copy efficiency test, the T710 delivers 790 MB/s per watt, nearly 99% higher than the T705’s 397 MB/s per watt. This efficiency comes from significantly lower power draw, as the T710 averages just 3 watts versus the T705’s 7 watts, a 57% reduction. Idle power usage also favors the T710 at 1,619 mW compared to 2,706 mW, a 40% decrease, making it more suitable for energy-conscious systems. Even under peak load, the T710 consumes only 8.80 watts, which is 23% lower than the T705’s 11.46 watts. These results highlight the T710 as not only the more powerful drive but also the far more power-efficient option, offering better performance per watt across the board.
Endurance, TBW, DWPD, and Warranty
| Specificiation | Crucial T705 | Crucial T710 |
|---|---|---|
| TBW (Terabytes Written) | 1TB: 600 TBW 2TB: 1200 TBW 4TB: 2400 TBW | 1TB: 600 TBW 2TB: 1200 TBW 4TB: 2400 TBW |
| DWPD (Drive Writes per Day) | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| MTBF (Mean Time Between Failure) | 1.5 Million Hours | 1.5 Million Hours |
| Warranty | 5 Years Limited | 5 Years Limited |
The TBW, MTBF, and DWPD are the same in both SSDs. It is good for T705 buyers because they don’t have to compromise on the endurance at a lower price.
Technical Specifications Comparison
| Specification | Crucial T705 | Crucial T710 |
|---|---|---|
| Controller | Phison’s PS5026-E26 | Silicon Motion SM2508 |
| Controller Architecture | ARM 32-bit Cortex-R5 + AndesCore 32-bit N25F RISC-V (5-Core) | ARM 32-bit Cortex-R8 + ARM 32-bit Cortex-M0 (5-Core) |
| DRAM Specifications | Micron’s LPDDR4 DRAM 1TB: 1×1024 MB 2TB: 1×2048 MB 4TB: 1x 4096 MB | Micron’s LPDDR4-4266 1TB: 1×1024 MB 2TB: 1×2048 MB 4TB: 1x 4096 MB |
| SLC Write Cache | 1TB: approx. 110 GB (dynamic only) 2TB: approx. 220 GB (dynamic only) 4TB: approx. 440 GB (dynamic only) | 1TB: – 2TB: approx. 368 GB (dynamic only) 4TB: – |
| NAND Flash | Micron’s B58R FortisFlash TLC | Micron’s B68S FortisFlash |
| Topology | 232-Layers | 276-layer |
| NAND speed | 2400 MT/s | 3600 MT/s |
| Read Time (tR)/Program Time (tProg) | 61 µs/600 µs | 32 µs/320 µs |
| Die Read Speed | 1574 MB/s | – |
| Die Write Speed | 160 MB/s | 300 MB/s |
| Encryption | AES-256, TCG Opal | AES-256, TCG Opal |
| Power Loss Protection | No | No |
| SMART/TRIM/PS5 Support | Yes/Yes/Yes | Yes/Yes/Yes |
The DRAM specifications are the same in the both, i.e., approximately 1GB per 1TB. This is a typical number.
For the Pseudo SLC Write cache, we have currently know the capacity only in the 2TB variant of the T710 which is 368 GB. This is 148 GB more from the 2TB variant of the T705. Surely, other variants of the T710 will have more SLC write cache, which clearly means a better handling of the incoming streams of write data in the T710.
Price Difference


By the time, I am writing this article, the 2TB variant of the T705 is available at $223.75 at NewEgg. The 2TB T710 is available for $298.75. So, I can save around $75 by choosing the T705, which offers slightly less performance but almost identical specs. The price difference is around 33% and this is the same for the 1TB and 4TB variants as well. However, prices keep changing, so if you see the T710 getting cheaper, you should definitely consider it to save some money while still enjoying better performance.
Final Verdict: Which one should you choose?
For the performance enthusiasts, with competent Gen 5.0 systems (including CPU and motherboard), the T710 is the best pick. T710 isn’t the fastest Gen 5.0, but it will definitely give you the feel of what a fast SSD can do. It is best for professional gamers, content creators, database handlers, or anyone seeking the fastest SSD speed. However, for most normal users, it is an overkill.
The T705, on the other hand, will offer you almost similar performance while saving you some money. Most people would not be able to see the difference between the two unless they use specified software to benchmark these SSDs. For normal tasks, gaming, and video editing, etc, the T705 is enough. I would say, for most people, the T705 is more than enough.
Go for the T710 only if you have enough budget to spend and you want to experience the top Gen 5.0 performance. Otherwise, the T705 is more than enough for most people.
I hope this helps!