Affiliate Disclosure: This post may include affiliate links. If you click and make a purchase, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
CMR (Classic Mechanical Recording) and SMR (Shingled Magnetic Recording) are hard drive data recording technologies with varying advantages. In another article about the working of hard drives, I discussed the SMR and CMR writing technologies a little. But, today, we are going to cover this topic in complete detail.
If you ever try to buy any kind of hard drive for storage purposes, you’ll see the options to choose between the CMR and SMR. CMR is known for its benefits in high-write applications, RAID/NAS setups, and enterprise environments. CMR is good where performance and frequent write operations are required. On the other hand, SMR is known best for archival storage, backups, and other applications where frequent write operations are not required.
The basic difference between CMR and SMR is how the data is written on the magnetic platter. The read/write heads are designed in a way that they make use of the platter for different benefits in their own ways. Let’s discuss the differences in detail.

The Working of the Hard Drives
The hard drives store the data on the magnetic platters. The most basic storage unit is a magnetic domain whose polarity can be changed from one direction to another. To write the data, these magnetic domains are charged in two possible positions in order to indicate bits of information. Below is the simplified image of how the data is written to a hard drive.

The write head applies the charge to a magnetic domain to change its polarity. However, the polarity of a domain doesn’t represent any data. To read a bit of data, the magnetic field between the two adjacent magnetic domains is checked. Below is a simplified image of how the data is read from a hard drive.
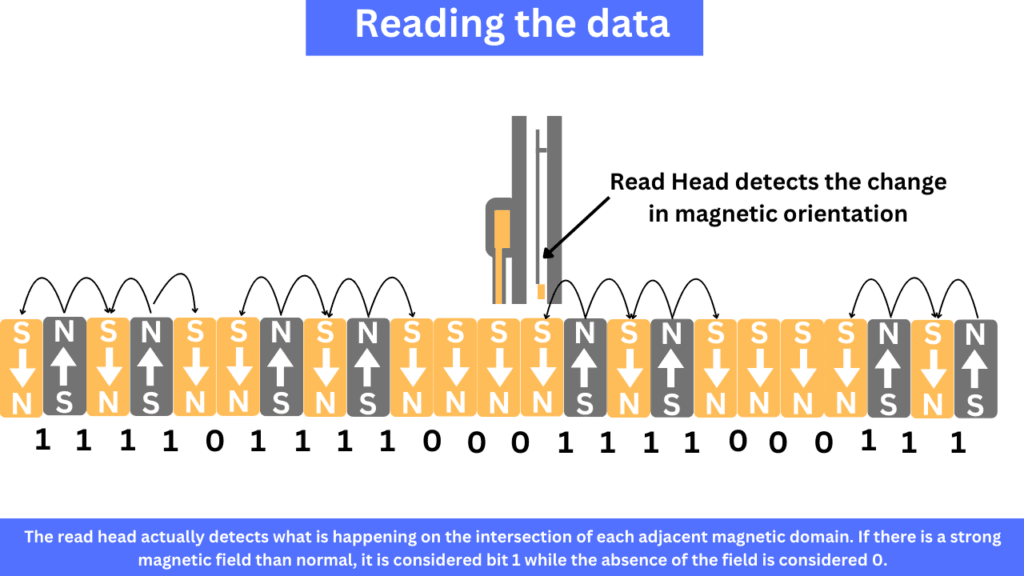
According to the coming data from the host, the write head changes the polarities of the magnetic domains so that the appropriate magnetic field is created. We can simply say that two magnetic domains are required to read or write one bit of the data. Basically, the intersection of two domains is where one bit is stored in the form of the magnetic field.
Magnetic domains are very tiny spaces and a single sector of hard drive (4KB) can have thousands to millions of magnetic domains. This depends on the storage density and the technology of the hard drive. Now, there are no physical markings on the platter to divide it into tracks and sectors. It is the job of the read/write head to write the platter in the way it is designed by the manufacturer. There are two ways a hard drive platter can be used to record the data i.e. CMR and SMR.
What is CMR?
CMR or Classic Magnetic Recording is the traditional method of reading and writing data in hard drives. The magnetic platter is divided into tracks and sectors more uniformly with perfect divisions. The space used for dividing these sectors and tracks is just for separation and nothing else. So, this space can be considered as wasted. When writing the data, the write head has some extra space to easily recognize the sectors from different tracks. We can take an example of a notebook where each line is properly divided using a hard line to create space for writing.

The biggest benefit of this type of recording is the head can independently read or write any sector in any track without interfering with others. The data can be written or overwritten without much complexity because each line is separated properly.

You can clearly see that the sector is properly divided with a space which makes it easy to access this specific sector without causing any interference to others. However, the drawback can also be seen which is the wasted platter space because of these divisions.
CMR benefits and drawbacks
The biggest benefit of CMR is that it is much more reliable and fast when we write the data. This is simply because the sectors are properly divided with empty space that tells the read/write heads its boundaries. Especially when the data has to be written in two adjacent tracks, the head can easily identify it and write directly without any issues. The CMR hard drives are most effective when there is a heavy write load. We can’t compare them with the write speed of the SSDs but as compared to the SMR hard drives, SMRs generally have a better write performance. This makes them best for high-load environments such as RAID, NAS, Backups, redundancy, and many other enterprise environments. You will see that most of the enterprise-level hard drives such as the Seagate Ironwold, Toshiba N300, and WD Red Plus come in the CMR technology because it is more reliable and write-performance-oriented.
The CMR hard drives are better in terms of data reliability because there are separations between sectors which make sure the data is properly intact. Also, the ECC can work pretty well when there are no chances of interference. The write operations are much more simpler in CMR which allows for precise writing and straightforward design.
As we discussed above, the sector separations will waste some space. This reduces a hard drive’s overall storage capacity but is surely good in performance-oriented environments. Also, the CMR hard drives are expensive and designed only for performance-oriented environments. However, because these drives are mostly used in the enterprise environments
What is SMR?
SMR or Shingled Magnetic Recording utilizes the magnetic platter surface much more efficiently. It increases the total storage space using the same physical storage space but has some drawbacks, especially during write operations. Overlapping sectors means there is no empty space horizontally between each sector. Instead, they are overlapped and sharing space with each other. However, there are separations in the vertical line separating each sector from each other.

So, you would say, why does this overlapping work because it can interfere with the sectors over or below each other. So, there are some important things to know. SMR hard drives use one-way shingles means one track will overlap just one track which is generally below it on the platter.
When writing the data, it is written first to the track which is at the bottom in two tracks. Only once the first track is written the overlapped track is written. It is like layering your roof with tiles, starting from the drop edge to the ridge. So, basically, the data is written layer by layer but we can store more data because of this overlapping. Now, because each sector is sharing some space with another sector, the read head must be precise and only read from the center of the sector and not from the overlapping part of another sector.
SMR benefits and drawbacks
First of all, we must understand the drawbacks. The SMR will offer much higher storage space in the same platter but has bad re-write performance especially when it is random data. I said re-write because you now know that if the data has to be written to any sector, the overlapping sector must be erased first and its valid data must be stored somewhere else (generally in the DRAM cache). Once, the overlapping layer is stored somewhere else, the actual layer can be re-written. Now, if we have to write random information in scattered locations, this process will be much more complex and the performance would reduce a lot more than usual. The sequential write performance can be a little better than the random write but not as good as an SMR hard drive.

The biggest benefit of Shingled Magnetic Recording is its high storage density. SMR utilizes platter space much more efficiently than CMR. But, there are surely some compromises to the write performance. This makes the SMR hard drives good for archival storage and low-budget systems. In fact, most consumer hard drives even the expensive ones use SMR technology. It is just that when we compare the working mechanism of both side by side, the SMR looks more complex and slow but in real life, the difference isn’t that much.
How to check if an SSD uses CMR or SMR?
In most cases, the CMR hard drives would be mentioned clearly on their product and eCommerce pages. However, if it is an SMR, you may have to do a little work. The best way is to check the datasheet by visiting the official website. In the specifications section, check for the Recording Technology section.

If you don’t find this information in the datasheet, you can check for the online reviews.
Which one is best for you? CMR or SMR
As we discussed earlier, most consumer hard drives use SMR technology because it is much more efficient in terms of storage density and still offers acceptable performance in less demanding workplaces. However, most enterprise-level hard drives will have the CMR technology. So, you generally don’t have a lot of options to choose from.
CMR vs SMR hard drive for Personal Usage
SMR is enough for personal and office computers for raw data storage. I said raw data storage because we shouldn’t forget that SSDs have almost replaced hard drives when it comes to operating system drives. However, if you want to have a hard drive for raw data storage or backups they are enough for that work.
CMR vs SMR hard drive for NAS/RAID
Personal and even the office NAS or RAID can work perfectly fine with the SMR hard drives. But, there are separate NAS hard drives in the markets that are made for that purpose. So, it is better if you use them as compared to SMR hard drives. If you are going to set up the NAS for heavy read/write operations in a demanding environment, it is surely better to for for a CMR instead of an SMR hard drive.
I hope this helps!