Affiliate Disclosure: This post may include affiliate links. If you click and make a purchase, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
There are many reasons you should use a hard drive for archival storage and data backups. When comparing hard drives to Solid State Drives, in terms of cost, storage density, and reliability, hard drives are generally considered superior in most areas. They surely have some drawbacks, but I would still like to discuss their effectiveness in terms of raw data storage, such as backups and databases. etc.
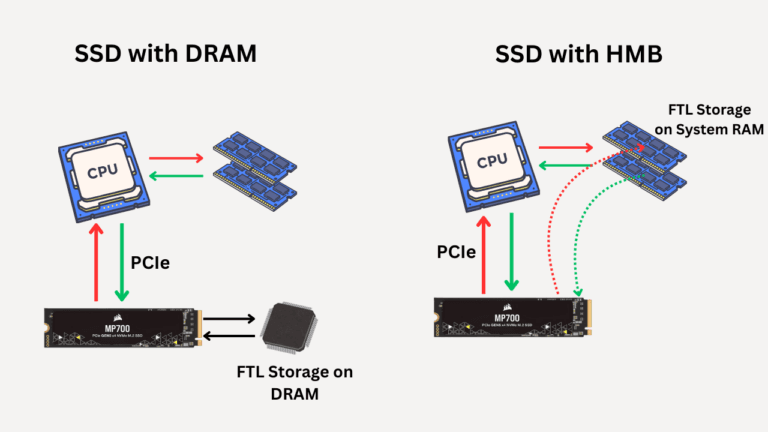
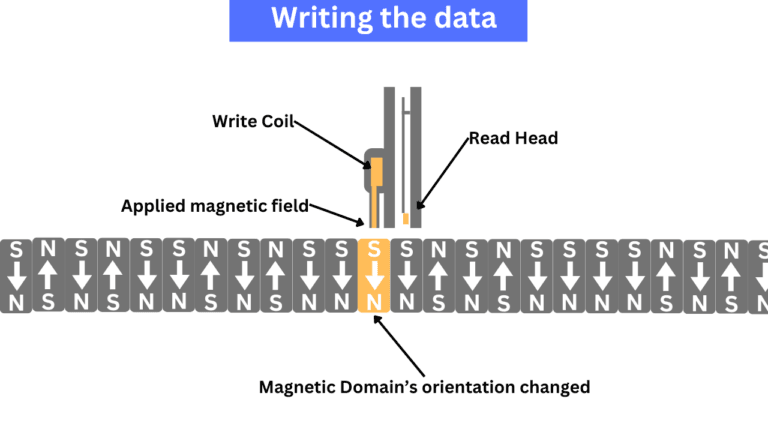
I am not saying SSDs aren’t reliable, but their basic storage functionality differs, and SSDs have more fragile or unstable methods of storing data as compared to hard drives. Hard drives, with the help of magnetic material as their storage medium, tend to store data in a much more effective manner. SSDs, on the other hand, store data in the form of electric charge, which eventually leaks out if SSDs remain without power for long periods. Modern SSDs, especially those with 3D NAND and charge-trap flash storage, offer greater resilience and charge-holding capabilities. However, hard drives are still considered more reliable for long-term data storage.

Understanding the AFR
If you check studies that compare the reliability of storage devices, most of them conclude that SSDs are more reliable than hard drives, though these studies are mainly for enterprise drives. However, most of these studies are conducted in large data centers and on enterprise SSDs (primarily SLC). Definitely, an SLC would beat any hard drive in terms of both performance and data retention. But this isn’t the case with consumer drives.
Most studies consider the AFR (Annual Failure Rate) a crucial criterion for determining an SSD’s reliability. AFR represents the percentage of devices that are expected to fail in one year out of the total number of devices. If an SSD has an AFR of 1%, this means that out of 1,000 SSDs, approximately 10 are expected to fail in a year.
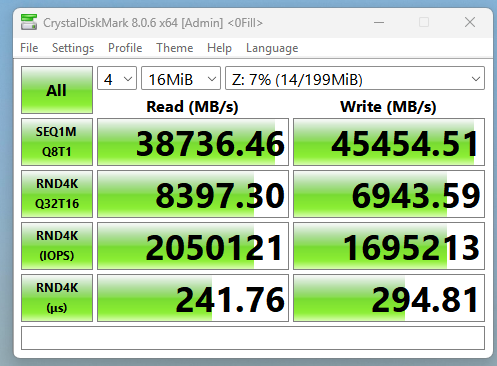
The very popular BackBlaze studies on both HDD and SSD conclude that SSDs are more reliable, with the average AFR (Annual Failure Rate) of SSDs being 1% throughout the 4 years of this study. In previous years, the hard drives were yielding AFR numbers as high as 5.23% and even 6.93%. As of 2025, the lifetime AFR had declined slightly from 1.31% (Q1 2025) to 1.30% with a total of 321,201 hard drives. However, this study is being conducted on specific drives and their corresponding models. Conducting this type of study is challenging due to the numerous different drives and their various models from multiple brands.
Benefits of Hard Drive for Raw Data Storage
Hard Drives are good in terms of cost-to-store density ratio as compared to solid-state drives. However, there are some specific benefits that you can only get with hard drives. Let’s discuss them.
1. Hard Drives Preserve Raw Data Reliably Over the Long Term
For archival storage, data longevity is perhaps the most important thing to consider. Typically, Hard Drives can last 5 to 10 years when used properly and stored in optimal conditions. Cool and dry environments are beneficial to long-term data storage. Compared to SSDs, Hard Drives can hold data for longer when stored without power. This is due to the magnetic storage medium, which is less susceptible to degradation when power is not present.
Hard Drives mostly fail due to mechanical failures, which can easily be avoided with proper care. Since there is no charge leakage, there is no charge loss in hard drives. Additionally, write operations are less destructive to memory blocks in a hard drive compared to SSDs. This problem is even worse when we use QLC drives for long-term raw data storage.
2. Ideal for Repetitive Read/Write Tasks Without Longevity Concerns
SSDs come with a limited number of Program/Erase cycles, which, when surpassed, make the SSDs less reliable for data storage. Hard Drives can also degrade with prolonged use, but the effects aren’t very intense. So, you can trust a used hard drive for long-term storage than a used SSD. Mechanical Drives Withstand Heavy Read/Write Workloads Reliably, and hence they can be trusted for long-term storage even after years of usage.
3. Mechanical Storage Reduces Risk of Silent Data Corruption
The magnetic storage nature of hard drives makes them more reliable due to their stability. Bit rot (because of high temperature, humidity, and magnetic fields) can easily be avoided with proper management of your drive. The ECCs work well while reading the data because of have only two magnetic fields.
4. Ease of Data Recovery
As long as the magnetic platter of your hard drive is in good condition, the data from a failing drive can be easily recovered. Being a mature storage technology, hard drives now offer significantly improved data recovery services.
5. High Capacity at Low Price
Hard Drives cost approximately $15-$25 per TB for consumer-grade drives (high-capacity models can go as low as $15/TB). A typical consumer SSD can cost you between $70 and $100. Overall, SSDs cost nearly 300-500% more per TB compared to Hard Drives. This makes the hard drives more practical for long-term, large-scale archival storage.
Things to Remember for using hard drives for cold storage
The most important thing is to store your drive in an optimal condition. Using your hard drive in a cool and dry environment is recommended. Additionally, keeping it away from dust and vibration is beneficial. Spin up your archival drives periodically, every few years or months, to check for mechanical functionality and ensure the data remains accessible. Because hard drives are cheaper, it is easy to set up RAID (in case of hot storage) or use multiple copies of your data in different drives (in case of cold storage).